The landscape of selection in 551 esophageal adenocarcinomas defines genomic biomarkers for the clinic
- PMID: 30718927
- PMCID: PMC6420087
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-018-0331-5
The landscape of selection in 551 esophageal adenocarcinomas defines genomic biomarkers for the clinic
Abstract
Esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) is a poor-prognosis cancer type with rapidly rising incidence. Understanding of the genetic events driving EAC development is limited, and there are few molecular biomarkers for prognostication or therapeutics. Using a cohort of 551 genomically characterized EACs with matched RNA sequencing data, we discovered 77 EAC driver genes and 21 noncoding driver elements. We identified a mean of 4.4 driver events per tumor, which were derived more commonly from mutations than copy number alterations, and compared the prevelence of these mutations to the exome-wide mutational excess calculated using non-synonymous to synonymous mutation ratios (dN/dS). We observed mutual exclusivity or co-occurrence of events within and between several dysregulated EAC pathways, a result suggestive of strong functional relationships. Indicators of poor prognosis (SMAD4 and GATA4) were verified in independent cohorts with significant predictive value. Over 50% of EACs contained sensitizing events for CDK4 and CDK6 inhibitors, which were highly correlated with clinically relevant sensitivity in a panel of EAC cell lines and organoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

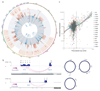
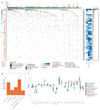


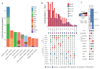
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015 Mar 1;136(5):E359–386. - PubMed
-
- Coleman HG, Xie SH, Lagergren J. The Epidemiology of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2018 Jan;154(2):390–405. - PubMed
-
- Campbell PJ, Getz G, Stuart JM, Korbel JO, Stein LD. Pan-cancer analysis of whole genomes. bioRxiv. 2017
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

