Rethinking Addiction
- PMID: 30719491
- PMCID: PMC6348542
- DOI: 10.1177/2333794X18821943
Rethinking Addiction
Abstract
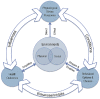
Addiction is a complex and challenging condition with many contributing factors. Although addictive behaviors appear to be individual choices, behavior alterations cannot be addressed successfully without considering characteristics of the physical and social environments in which individuals live, work, and play. Exposure to chronic psychosocial stressors and the physiological response of individuals to their external environment activates the brain's neuroendocrine hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, with profound conditioning effects on behavior. This brief synopsis describes the social determinants of health; examines the interconnectedness of the psychosocial environment, behavior, and subsequent health outcomes; discusses the environment's critical influence on brain plasticity, adaptation and functioning; and explores additional factors that complicate adolescent addiction. Because the environment is both a determinant of behavior and an opportunity for intervention, in the context of addictions, it is important to incorporate these factors in the analysis of risk and design of early interventions for prevention and amelioration of addiction.
Keywords: addiction; adolescents; brain plasticity; psychosocial stressors; social determinants of health.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Shonkoff JP, Garner AS; Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health; Committee on Early Childhood, Adoption, and Dependent Care; Section on Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics. The lifelong effects of early childhood adversity and toxic stress. Pediatrics. 2012;129:e232-e246. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-2663 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

