Observational study of newborn infant parasympathetic evaluation as a comfort system in awake patients admitted to a pediatric intensive care unit
- PMID: 30721390
- PMCID: PMC7088066
- DOI: 10.1007/s10877-019-00268-1
Observational study of newborn infant parasympathetic evaluation as a comfort system in awake patients admitted to a pediatric intensive care unit
Abstract
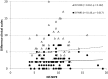
To compare the newborn infant parasympathetic evaluation system (NIPE) scores with a validated clinical scale using two different nebulizers in children with bronchiolitis admitted to a PICU. Comfort was evaluated using the COMFORT-behavior scale (CBS) before (T1), during (T2) and after (T3) each nebulization. In order to compare NIPE and CBS values during the whole T1 to T3 period, the variable Dif-CBS was defined as the difference between maximal and minimal CBS scores, and Dif-NIPE as the difference between 75th and 25th percentile NIPE values. Analyses were carried out, firstly for the total of nebulizations and secondly comparing two different nebulization systems: a jet nebulizer (JN) and a nebulizer integrated in high flow nasal cannulas (NHF). 84 nebulizations were recorded on 14 patients with a median [25th-75th percentile] age of 6 months (3.1-9.5). A Dif-CBS of 4 points (2-7), as well as changes in CBS scores between T1 and T2, defined the nebulization as a discomfort stimulus. The NIPE system, represented as the Dif-NIPE, showed a median variation of 9 points (7-10), and was poorly correlated to Dif-CBS [rs 0.162 (P = 0.142)]. Discomfort during nebulization, assessed by CBS was greater with the JN system compared to NHF: 17 (13-22) vs 13 (9-15) (P = 0.001). NIPE monitoring detected no significant differences between both nebulization systems (P = 0.706). NIPE monitoring showed a variation in comfort during nebulization in the patient with bronchiolitis, though correlation with CBS was poor. Further research is required before NIPE can be suggested as a comfort monitoring system for the awake infant.
Keywords: Bronchiolitis; COMFORT Behavior Scale; Comfort; Nebulization; Newborn infant parasympathetic evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest declared.
Figures
Comment in
-
NIPE is related to parasympathetic activity. Is it also related to comfort?J Clin Monit Comput. 2019 Oct;33(5):747-748. doi: 10.1007/s10877-019-00276-1. Epub 2019 Feb 13. J Clin Monit Comput. 2019. PMID: 30758689 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ralston SL, Lieberthal AS, Meissner HC, Alverson BK, Baley JE, Gadomski AM, Johnson DW, Light MJ, Maraqa NF, Mendonca EA, Phelan KJ, Zorc JJ, Stanko-Lopp D, Brown MA, Nathanson I, Rosenblum E, Sayles S, 3rd, Hernandez-Cancio S, American Academy of Pediatrics Clinical practice guideline: the diagnosis, management, and prevention of bronchiolitis. Pediatrics. 2014;134(5):e1474–e1502. doi: 10.1542/peds.2014-2742. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources