Development and In Vivo Evaluation of Ziyuglycoside I-Loaded Self-Microemulsifying Formulation for Activity of Increasing Leukocyte
- PMID: 30721444
- PMCID: PMC6373417
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-019-1313-3
Development and In Vivo Evaluation of Ziyuglycoside I-Loaded Self-Microemulsifying Formulation for Activity of Increasing Leukocyte
Abstract
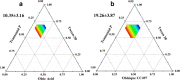
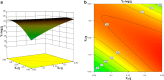
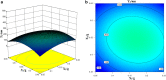
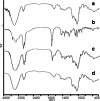
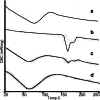
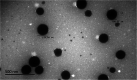
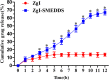
Ziyuglycoside I (ZgI), a major effective ingredient of Sanguisorba officinalis L, has shown good activity in increasing leukocyte of myelosuppression mice. However, oral ZgI therapy has been deterred by poor bioavailability because of its low aqueous solubility and permeability. Our study was to develop ZgI-loaded self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) and evaluate its intestinal absorption, and pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic activity for increasing leukocyte. The formulation was designed and optimized by measuring the equilibrium solubility of ZgI in different vehicles and the pseudoternary phase diagram. Further, morphology, particle size, stability, in vitro release, in situ single-pass intestinal perfusion (SPIP), in vivo activity, and in vivo pharmacokinetic (PK) of ZgI-SMEDDS were charactered or studied. Optimized formulations for in vitro dissolution were Obleique CC497, Tween-20, and Transcutol HP with a proportion of 0.25/0.45/0.30 via D-optimal mixture design. Results showed that the solubility of ZgI was enhanced up to 23.93 mg/g and its average particle size was 207.92 ± 2.13 nm. The release of ZgI had been greatly improved by the SMEDDS. In SPIP, the intestinal absorption of SMEDDS was much better than plain ZgI. In PK, we found the oral bioavailability of ZgI-SMEDDS was 6.94-fold higher absolute bioavailability (21.94 ± 4.67) % than ZgI (3.16 ± 0.89) %. The most important was that the mice WBC of ZgI-SMEDDS group was significantly higher than that of the ZgI group. Our study suggested that SMEDDS could increase the solubility of ZgI, which was beneficial to improve oral bioavailability and enhance biological activity.
Keywords: SMEDDS; bioavailability; solubility; ziyuglycoside I.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel Drug Delivery Approach via Self-Microemulsifying Drug Delivery System for Enhancing Oral Bioavailability of Asenapine Maleate: Optimization, Characterization, Cell Uptake, and In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Studies.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019 Jan 7;20(2):44. doi: 10.1208/s12249-018-1212-z. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019. PMID: 30617712
-
Solid Self-Microemulsifying Drug Delivery System for Improved Oral Bioavailability of Relugolix: Preparation and Evaluation.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jan 25;20:1065-1082. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S497099. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 39886543 Free PMC article.
-
Quality-by-design based development of a self-microemulsifying drug delivery system to reduce the effect of food on Nelfinavir mesylate.Int J Pharm. 2016 Mar 30;501(1-2):311-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.02.008. Epub 2016 Feb 6. Int J Pharm. 2016. PMID: 26854426
-
Self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems (SMEDDS) for improving in vitro dissolution and oral absorption of Pueraria lobata isoflavone.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2005 May;31(4-5):349-56. doi: 10.1081/ddc-54309. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2005. PMID: 16093200
-
Self-micro Emulsifying Drug Delivery via Intestinal Lymphatics: A Lucrative Approach to Drug Targeting.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2023 Jun 6;11(3):238-264. doi: 10.2174/2211738511666230112123235. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37293951 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of an Oral Isoliquiritigenin Self-Nano-Emulsifying Drug Delivery System (ILQ-SNEDDS) for Effective Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis Induced by Food Allergy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Dec 19;15(12):1587. doi: 10.3390/ph15121587. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36559038 Free PMC article.
-
Gold Nanoparticles Coated with SH-PEG-NH2 and Loaded with Ziyuglycoside I for Promoting Autophagy in Hematopoietic Stem Cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Mar 21;18:1347-1362. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S399568. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 36974074 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an Orally Bioavailable Isoliquiritigenin Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System to Effectively Treat Ovalbumin-Induced Asthma.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Nov 13;15:8945-8961. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S269982. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33223829 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in drug delivery systems: Work in progress still needed?Int J Pharm X. 2020 Jun 12;2:100050. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2020.100050. eCollection 2020 Dec. Int J Pharm X. 2020. PMID: 32577616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TPGS-Modified Long-Circulating Liposomes Loading Ziyuglycoside I for Enhanced Therapy of Myelosuppression.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Sep 14;16:6281-6295. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S326629. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34548791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bazan JG, Luxton G, Mok EC, et al. Normal tissue complication probability modeling of acute hematologic toxicity in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the anal canal treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy[J] Int J Radiat Oncol. 2011;81(2):S126. - PubMed
-
- Dai LM, Xiong YA, Yang M, et al. Protective effects of dioscin saponins on mice myelosuppression induced by cyclophosphamide. Nat Prod Res Dev. 2016;28(6):852–859.
-
- Su ZT, Liu Y, Yang M, et al. Optimization of flash extraction process of saponins from Radix Scutellariae by Box-Behnken design. CHM. 2012;43(3):501–504.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

