The Cortical Neuroimmune Regulator TANK Affects Emotional Processing and Enhances Alcohol Drinking: A Translational Study
- PMID: 30721969
- PMCID: PMC6430980
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhy341
The Cortical Neuroimmune Regulator TANK Affects Emotional Processing and Enhances Alcohol Drinking: A Translational Study
Abstract
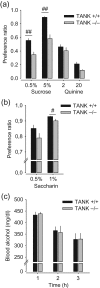
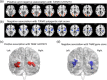
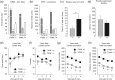
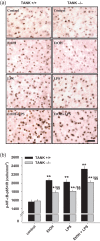
Alcohol abuse is a major public health problem worldwide. Understanding the molecular mechanisms that control regular drinking may help to reduce hazards of alcohol consumption. While immunological mechanisms have been related to alcohol drinking, most studies reported changes in immune function that are secondary to alcohol use. In this report, we analyse how the gene "TRAF family member-associated NF-κB activator" (TANK) affects alcohol drinking behavior. Based on our recent discovery in a large GWAS dataset that suggested an association of TANK, SNP rs197273, with alcohol drinking, we report that SNP rs197273 in TANK is associated both with gene expression (P = 1.16 × 10-19) and regional methylation (P = 5.90 × 10-25). A tank knock out mouse model suggests a role of TANK in alcohol drinking, anxiety-related behavior, as well as alcohol exposure induced activation of insular cortex NF-κB. Functional and structural neuroimaging studies among up to 1896 adolescents reveal that TANK is involved in the control of brain activity in areas of aversive interoceptive processing, including the insular cortex, but not in areas related to reinforcement, reward processing or impulsiveness. Our findings suggest that the cortical neuroimmune regulator TANK is associated with enhanced aversive emotional processing that better protects from the establishment of alcohol drinking behavior.
Keywords: NF-κB; TANK; alcohol; anxiety; drinking; insular cortex.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TRAF Family Member-associated NF-κB Activator (TANK) Inhibits Genotoxic Nuclear Factor κB Activation by Facilitating Deubiquitinase USP10-dependent Deubiquitination of TRAF6 Ligase.J Biol Chem. 2015 May 22;290(21):13372-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.643767. Epub 2015 Apr 10. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25861989 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF family member-associated NF-κB activator (TANK) is a negative regulator of osteoclastogenesis and bone formation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 17;287(34):29114-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.347799. Epub 2012 Jul 6. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22773835 Free PMC article.
-
Encephalomyocarditis Virus 3C Protease Relieves TRAF Family Member-associated NF-κB Activator (TANK) Inhibitory Effect on TRAF6-mediated NF-κB Signaling through Cleavage of TANK.J Biol Chem. 2015 Nov 13;290(46):27618-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.660761. Epub 2015 Sep 11. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26363073 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroimmune Function and the Consequences of Alcohol Exposure.Alcohol Res. 2015;37(2):331-41, 344-51. Alcohol Res. 2015. PMID: 26695754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Acute or Chronic Alcohol Intake on the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Alcohol-Related Liver Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 10;21(24):9407. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249407. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33321885 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic ethanol induces a pro-inflammatory switch in interleukin-1β regulation of GABAergic signaling in the medial prefrontal cortex of male mice.Brain Behav Immun. 2023 May;110:125-139. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2023.02.020. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Brain Behav Immun. 2023. PMID: 36863493 Free PMC article.
-
Neutral sphingomyelinase mediates the co-morbidity trias of alcohol abuse, major depression and bone defects.Mol Psychiatry. 2021 Dec;26(12):7403-7416. doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01304-w. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Mol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34584229 Free PMC article.
-
Self-management with alcohol over lifespan: psychological mechanisms, neurobiological underpinnings, and risk assessment.Mol Psychiatry. 2023 Jul;28(7):2683-2696. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02074-3. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Mol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37117460 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol and the brain: from genes to circuits.Trends Neurosci. 2021 Dec;44(12):1004-1015. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2021.09.006. Epub 2021 Oct 23. Trends Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34702580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal lipofuscinosis caused by Kufs disease/CLN4 DNAJC5 mutations but not by a CSPα/DNAJC5 deficiency.Sci Adv. 2025 May 23;11(21):eads3393. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ads3393. Epub 2025 May 21. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40397740 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

