Shared polygenic risk and causal inferences in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- PMID: 30723964
- PMCID: PMC6450729
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.25431
Shared polygenic risk and causal inferences in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Erratum in
-
Correction.Ann Neurol. 2020 Jun;87(6):991-992. doi: 10.1002/ana.25727. Epub 2020 Apr 25. Ann Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32437083 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
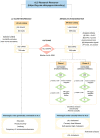
Objective: To identify shared polygenic risk and causal associations in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Methods: Linkage disequilibrium score regression and Mendelian randomization were applied in a large-scale, data-driven manner to explore genetic correlations and causal relationships between >700 phenotypic traits and ALS. Exposures consisted of publicly available genome-wide association studies (GWASes) summary statistics from MR Base and LD-hub. The outcome data came from the recently published ALS GWAS involving 20,806 cases and 59,804 controls. Multivariate analyses, genetic risk profiling, and Bayesian colocalization analyses were also performed.
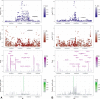
Results: We have shown, by linkage disequilibrium score regression, that ALS shares polygenic risk genetic factors with a number of traits and conditions, including positive correlations with smoking status and moderate levels of physical activity, and negative correlations with higher cognitive performance, higher educational attainment, and light levels of physical activity. Using Mendelian randomization, we found evidence that hyperlipidemia is a causal risk factor for ALS and localized putative functional signals within loci of interest.
Interpretation: Here, we have developed a public resource (https://lng-nia.shinyapps.io/mrshiny) which we hope will become a valuable tool for the ALS community, and that will be expanded and updated as new data become available. Shared polygenic risk exists between ALS and educational attainment, physical activity, smoking, and tenseness/restlessness. We also found evidence that elevated low-desnity lipoprotein cholesterol is a causal risk factor for ALS. Future randomized controlled trials should be considered as a proof of causality. Ann Neurol 2019;85:470-481.
© 2019 American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
B.J.T., P.J.T., and A.B.S. hold patents on the clinical testing and therapeutic intervention for the hexanucleotide repeat expansion of
Figures
Comment in
-
Smoking is a cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. High low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels? Unsure.Ann Neurol. 2019 Apr;85(4):465-469. doi: 10.1002/ana.25468. Ann Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30875450 No abstract available.
References
-
- Belbasis L, Bellou V, Evangelou E. Environmental risk factors and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: an umbrella review and critical assessment of current evidence from systematic reviews and meta‐analyses of observational studies. Neuroepidemiology 2016;46:96–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- Helsinki University Hospital/International
- MR/K01417X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 259867/European Community's Health Seventh Framework Programme/International
- Z99 AG999999/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- G-0907/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- ALS Association/International
- Sigrid Jusélius Foundation/International
- ZIA AG000933/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- University of Turin (Ricerca locale ex 60% 2016 and 2017)/International
- G0901254/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- Target ALS Multicenter Postmortem Core/International
- ZIA AG000933-03/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- Microsoft Research/International
- P01 AG017586/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L501542/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RF-2016-02362405/Italian Ministry of Health/International
- K24 AG000949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 208806/Z/17/Z/Royal Society/International
- MR/N026004/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- Joint Programme Neurodegenerative Disease Research (JPND)/International
- Fondazione Vialli e Mauro onlus/International
- Canadian Consortium on Neurodegeneration in Aging (ER)/International
- Z01 AG000949/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- Muscular Dystrophy Association/International
- NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- Packard Center for ALS Research at Johns Hopkins/International
- Barts Charity (Preventive Neurology Unit)/International
- G0701075/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention/International
- Italian Ministry of University/International
- RF-2010-2309849/Italian Ministry of Health/International
- Intramural Research Program of the NIH/International
- Merck & Co., Inc./International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

