Fourth generation e-cigarette vaping induces transient lung inflammation and gas exchange disturbances: results from two randomized clinical trials
- PMID: 30724099
- PMCID: PMC6589591
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00492.2018
Fourth generation e-cigarette vaping induces transient lung inflammation and gas exchange disturbances: results from two randomized clinical trials
Abstract
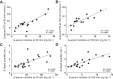
When heated by an electronic cigarette, propylene glycol and glycerol produce a nicotine-carrying-aerosol. This hygroscopic/hyperosmolar aerosol can deposit deep within the lung. Whether these deposits trigger local inflammation and disturb pulmonary gas exchanges is not known. The aim of this study was to assess the acute effects of high-wattage electronic cigarette vaping with or without nicotine on lung inflammation biomarkers, transcutaneous gas tensions, and pulmonary function tests in young and healthy tobacco smokers. Acute effects of vaping without nicotine on arterial blood gas tensions were also assessed in heavy smokers suspected of coronary artery disease. Using a single-blind within-subjects study design, 25 young tobacco smokers underwent three experimental sessions in random order: sham-vaping and vaping with and without nicotine at 60 W. Twenty heavy smokers were also exposed to sham-vaping (n = 10) or vaping without nicotine (n = 10) in an open-label, randomized parallel study. In the young tobacco smokers, compared with sham-vaping: 1) serum club cell protein-16 increased after vaping without nicotine (mean ± SE, -0.5 ± 0.2 vs. +1.1 ± 0.3 µg/l, P = 0.013) and vaping with nicotine (+1.2 ± 0.3 µg/l, P = 0.009); 2) transcutaneous oxygen tension decreased for 60 min after vaping without nicotine (nadir, -0.3 ± 1 vs. -15.3 ± 2.3 mmHg, P < 0.001) and for 80-min after vaping with nicotine (nadir, -19.6 ± 2.8 mmHg, P < 0.001). Compared with sham vaping, vaping without nicotine decreased arterial oxygen tension for 5 min in heavy-smoking patients (+5.4 ± 3.3 vs. -5.4 ± 1.9 mmHg, P = 0.012). Acute vaping of propylene glycol/glycerol aerosol at high wattage with or without nicotine induces airway epithelial injury and sustained decrement in transcutaneous oxygen tension in young tobacco smokers. Intense vaping conditions also transiently impair arterial oxygen tension in heavy smokers.
Keywords: arterial oxygen tension; club cell protein-16; e-cigarette; transcutaneous oxygen tension.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures






Comment in
-
High-power vaping injures the human lung.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2019 May 1;316(5):L703-L704. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00099.2019. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30838866 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Arsalane K, Broeckaert F, Knoops B, Wiedig M, Toubeau G, Bernard A. Clara cell specific protein (CC16) expression after acute lung inflammation induced by intratracheal lipopolysaccharide administration. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 161: 1624–1630, 2000. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.161.5.9812157. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Miller MR, Hankinson J, Brusasco V, Burgos F, Casaburi R, Coates A, Crapo R, Enright P, van der Grinten CP, Gustafsson P, Jensen R, Johnson DC, MacIntyre N, McKay R, Navajas D, Pedersen OF, Pellegrino R, Viegi G, Wanger J; ATS/ERS Task Force . Standardisation of spirometry. Eur Respir J 26: 319–338, 2005. doi: 10.1183/09031936.05.00034805. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bernard AM, Moreau D, Lauwerys RR. Latex immunoassay of retinol-binding protein. Clin Chem 28: 1167–1171, 1982. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

