HIV-1 and SIV Infection Are Associated with Early Loss of Lung Interstitial CD4+ T Cells and Dissemination of Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- PMID: 30726727
- PMCID: PMC6417097
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.01.021
HIV-1 and SIV Infection Are Associated with Early Loss of Lung Interstitial CD4+ T Cells and Dissemination of Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Abstract
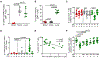
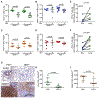
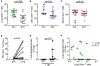
Lung interstitial CD4+ T cells are critical for protection against pulmonary infections, but the fate of this population during HIV-1 infection is not well described. We studied CD4+ T cells in the setting of HIV-1 infection in human lung tissue, humanized mice, and a Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb)/simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) nonhuman primate co-infection model. Infection with a CCR5-tropic strain of HIV-1 or SIV results in severe and rapid loss of lung interstitial CD4+ T cells but not blood or lung alveolar CD4+ T cells. This is accompanied by high HIV-1 production in these cells in vitro and in vivo. Importantly, during early SIV infection, loss of lung interstitial CD4+ T cells is associated with increased dissemination of pulmonary Mtb infection. We show that lung interstitial CD4+ T cells serve as an efficient target for HIV-1 and SIV infection that leads to their early depletion and an increased risk of disseminated tuberculosis.
Keywords: BAL; CD4+ T cells; HIV-1; HIV/TB co-infection; cell death; lung; tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Badley AD, Pilon AA, Landay A, and Lynch DH (2000). Mechanisms of HIV-associated lymphocyte apoptosis. Blood 96, 2951–2964. - PubMed
-
- Boutwell CL, Carlson JM, Lin TH, Seese A, Power KA, Peng J, Tang Y, Brumme ZL, Heckerman D, Schneidewind A, et al. (2013). Frequent and variable cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte escape-associated fitness costs in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype B Gag proteins. J. Virol 87, 3952–3965. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AI111914/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI123047/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI112521/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI040618/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI089323/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P51 OD011133/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R21 RR026006/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI060354/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F30 HL134566/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI123780/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL106790/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK043351/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI111943/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI040618/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL121827/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

