MicroRNA-7 as a potential therapeutic target for aberrant NF-κB-driven distant metastasis of gastric cancer
- PMID: 30728051
- PMCID: PMC6364399
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-019-1074-6
MicroRNA-7 as a potential therapeutic target for aberrant NF-κB-driven distant metastasis of gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: Dysregulated miR-7 and aberrant NF-κB activation were reported in various human cancers. However, the expression profile, clinical relevance and dysregulated mechanism of miR-7 and NF-κB RelA/p65 in human gastric cancers (GC) metastasis remain largely unknown. This study is to investigate the expression profile, clinical relevance and dysregulated mechanism of miR-7 and NF-κB RelA/p65 in GC and to explore the potential therapeutic effect of miR-7 to GC distant metastasis.
Methods: TCGA STAD and NCBI GEO database were used to investigate the expression profile of miR-7 and NF-κB RelA/p65 and clinical relevance. Lentivirus-mediated gene delivery was applied to explore the therapeutic effect of miR-7 in GC. Real-time PCR, FACS, IHC, IF, reporter gene assay, IP, pre-miRNA-7 processing and binding assays were performed.
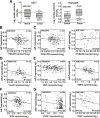
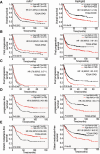
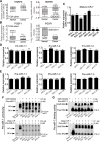
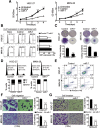
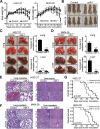
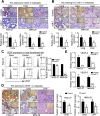
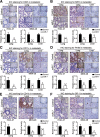
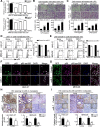
Results: Low miR-7 correlated with high RelA/p65 in GC with a clinical relevance that low miR-7 and high RelA/p65 as prognostic indicators of poor survival outcome of GC patients. Moreover, an impaired pre-miR-7 processing caused by dysregulated Dicer1 expression is associated with downregulated miR-7 in GC cells. Functionally, delivery of miR-7 displays therapeutic effects to GC lung and liver metastasis by alleviating hemangiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis as well as inflammation cells infiltration. Mechanistically, miR-7 suppresses NF-κB transcriptional activity and its downstream metastasis-related molecules Vimentin, ICAM-1, VCAM-1, MMP-2, MMP-9 and VEGF by reducing p65 and p-p65-ser536 expression. Pharmacologic prevention of NF-κB activator LPS obviously restored miR-7-suppressed NF-κB transcriptional activation and significantly reverted miR-7-inhibited cell migration and invasion.
Conclusions: Our data suggest loss of miR-7 in GC promotes p65-mediated aberrant NF-κB activation, facilitating GC metastasis and ultimately resulting in the worse clinical outcome. Thus, miR-7 may act as novel prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target for aberrant NF-κB-driven GC distant metastasis.
Keywords: Clinical outcome; Distant metastasis; Gastric Cancer; MiR-7; NF-κB.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All animal procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care Committee of Chongqing medical University (Chongqing, China).
Consent for publication
None.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-155-5p inhibition promotes the transition of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to gastric cancer tissue derived MSC-like cells via NF-κB p65 activation.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 29;7(13):16567-80. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7767. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26934326 Free PMC article.
-
miR-508-3p concordantly silences NFKB1 and RELA to inactivate canonical NF-κB signaling in gastric carcinogenesis.Mol Cancer. 2016 Jan 22;15:9. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0493-7. Mol Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26801246 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-7-5p inhibits melanoma cell proliferation and metastasis by suppressing RelA/NF-κB.Oncotarget. 2016 May 31;7(22):31663-80. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9421. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27203220 Free PMC article.
-
From inflammation to metastasis: The central role of miR-155 in modulating NF-κB in cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Jan;253:154962. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154962. Epub 2023 Nov 19. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 38006837 Review.
-
Therapeutic relevance of SOX9 stem cell factor in gastric cancer.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019 Feb;23(2):143-152. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2019.1559826. Epub 2018 Dec 20. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019. PMID: 30572738 Review.
Cited by
-
Matrix Metalloproteinases in Helicobacter pylori-Associated Gastritis and Gastric Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 8;23(3):1883. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031883. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NORAD-sponged miR-378c alleviates malignant behaviors of stomach adenocarcinoma via targeting NRP1.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Feb 14;22(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02474-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 35164743 Free PMC article.
-
The m6A Methyltransferase METTL14-Mediated N6-Methyladenosine Modification of PTEN mRNA Inhibits Tumor Growth and Metastasis in Stomach Adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Aug 12;11:699749. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.699749. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34476213 Free PMC article.
-
miR-181d/RBP2/NF-κB p65 Feedback Regulation Promotes Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Blast Crisis.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 25;11:654411. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.654411. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33842368 Free PMC article.
-
Antidiabetic Agent DPP-4i Facilitates Murine Breast Cancer Metastasis by Oncogenic ROS-NRF2-HO-1 Axis via a Positive NRF2-HO-1 Feedback Loop.Front Oncol. 2021 May 26;11:679816. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.679816. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34123848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism. and function Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

