Hypernatremia
- PMID: 30728169
- PMCID: PMC6419289
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.12141018
Hypernatremia
Keywords: Acids; Dehydration; Ions; Noncarboxylic; Potassium; Sodium; diabetes insipidus; diagnosis; hypernatremia; pathophysiology; sodium regulation; treatment; water regulation.
Figures
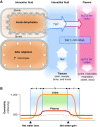
References
-
- Robertson GL: Diabetes insipidus: Differential diagnosis and management. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 30: 205–218, 2016 - PubMed
-
- Fenske W, Refardt J, Chifu I, Schnyder I, Winzeler B, Drummond J, Ribeiro-Oliveira A Jr, Drescher T, Bilz S, Vogt DR, Malzahn U, Kroiss M, Christ E, Henzen C, Fischli S, Tönjes A, Mueller B, Schopohl J, Flitsch J, Brabant G, Fassnacht M, Christ-Crain M: A copeptin-based approach in the diagnosis of diabetes insipidus. N Engl J Med 379: 428–439, 2018 - PubMed
-
- Timper K, Fenske W, Kühn F, Frech N, Arici B, Rutishauser J, Kopp P, Allolio B, Stettler C, Müller B, Katan M, Christ-Crain M: Diagnostic accuracy of copeptin in the differential diagnosis of the polyuria-polydipsia syndrome: A prospective multicenter study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100: 2268–2274, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Bolat F, Oflaz MB, Güven AS, Özdemir G, Alaygut D, Doğan MT, Içağasoğlu FD, Cevit Ö, Gültekin A: What is the safe approach for neonatal hypernatremic dehydration? A retrospective study from a neonatal intensive care unit. Pediatr Emerg Care 29: 808–813, 2013 - PubMed
-
- Alshayeb HM, Showkat A, Babar F, Mangold T, Wall BM: Severe hypernatremia correction rate and mortality in hospitalized patients. Am J Med Sci 341: 356–360, 2011 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

