Modulation of the sigma-1 receptor-IRE1 pathway is beneficial in preclinical models of inflammation and sepsis
- PMID: 30728287
- PMCID: PMC6936250
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aau5266
Modulation of the sigma-1 receptor-IRE1 pathway is beneficial in preclinical models of inflammation and sepsis
Erratum in
-
Erratum for the Research Article: "Modulation of the sigma-1 receptor-IRE1 pathway is beneficial in preclinical models of inflammation and sepsis" by D. A. Rosen, S. M. Seki, A. Fernández-Castañeda, R. M. Beiter, J. D. Eccles, J. A. Woodfolk, A. Gaultier.Sci Transl Med. 2019 Mar 27;11(485):eaax3130. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aax3130. Sci Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 30918112 No abstract available.
Abstract
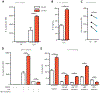
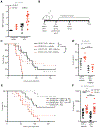
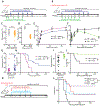
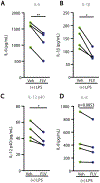
Sepsis is an often deadly complication of infection in which systemic inflammation damages the vasculature, leading to tissue hypoperfusion and multiple organ failure. Currently, the standard of care for sepsis is predominantly supportive, with few therapeutic options available. Because of increased sepsis incidence worldwide, there is an urgent need for discovery of novel therapeutic targets and development of new treatments. The recently discovered function of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in regulation of inflammation offers a potential avenue for sepsis control. Here, we identify the ER-resident protein sigma-1 receptor (S1R) as an essential inhibitor of cytokine production in a preclinical model of septic shock. Mice lacking S1R succumb quickly to hypercytokinemia induced by a sublethal challenge in two models of acute inflammation. Mechanistically, we find that S1R restricts the endonuclease activity of the ER stress sensor IRE1 and cytokine expression but does not inhibit the classical inflammatory signaling pathways. These findings could have substantial clinical implications, as we further find that fluvoxamine, an antidepressant therapeutic with high affinity for S1R, protects mice from lethal septic shock and dampens the inflammatory response in human blood leukocytes. Our data reveal the contribution of S1R to the restraint of the inflammatory response and place S1R as a possible therapeutic target to treat bacterial-derived inflammatory pathology.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures


References
-
- Cho JA, Lee AH, Platzer B, Cross BC, Gardner BM, De Luca H, Luong P, Harding HP, Glimcher LH, Walter P, Fiebiger E, Ron D, Kagan JC, Lencer WI, The unfolded protein response element IRE1alpha senses bacterial proteins invading the ER to activate RIG-I and innate immune signaling. Cell host & microbe 13, 558–569 (2013). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Qiu Q, Zheng Z, Chang L, Zhao YS, Tan C, Dandekar A, Zhang Z, Lin Z, Gui M, Li X, Zhang T, Kong Q, Li H, Chen S, Chen A, Kaufman RJ, Yang WL, Lin HK, Zhang D, Perlman H, Thorp E, Zhang K, Fang D, Toll-like receptor-mediated IRE1alpha activation as a therapeutic target for inflammatory arthritis. EMBO J 32, 2477–2490 (2013). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cubillos-Ruiz JR, Silberman PC, Rutkowski MR, Chopra S, Perales-Puchalt A, Song M, Zhang S, Bettigole SE, Gupta D, Holcomb K, Ellenson LH, Caputo T, Lee AH, Conejo-Garcia JR, Glimcher LH, ER Stress Sensor XBP1 Controls Anti-tumor Immunity by Disrupting Dendritic Cell Homeostasis. Cell 161, 1527–1538 (2015). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Urano F, Wang X, Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Chung P, Harding HP, Ron D, Coupling of stress in the ER to activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase IRE1. Science 287, 664–666 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

