Pharmacological reactivation of MYC-dependent apoptosis induces susceptibility to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy
- PMID: 30728358
- PMCID: PMC6365524
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-08541-2
Pharmacological reactivation of MYC-dependent apoptosis induces susceptibility to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Pharmacological reactivation of MYC-dependent apoptosis induces susceptibility to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy.Nat Commun. 2019 Feb 20;10(1):932. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08956-x. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30787321 Free PMC article.
Abstract
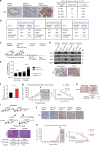
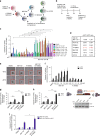
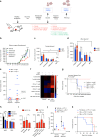
Elevated MYC expression sensitizes tumor cells to apoptosis but the therapeutic potential of this mechanism remains unclear. We find, in a model of MYC-driven breast cancer, that pharmacological activation of AMPK strongly synergizes with BCL-2/BCL-XL inhibitors to activate apoptosis. We demonstrate the translational potential of an AMPK and BCL-2/BCL-XL co-targeting strategy in ex vivo and in vivo models of MYC-high breast cancer. Metformin combined with navitoclax or venetoclax efficiently inhibited tumor growth, conferred survival benefits and induced tumor infiltration by immune cells. However, withdrawal of the drugs allowed tumor re-growth with presentation of PD-1+/CD8+ T cell infiltrates, suggesting immune escape. A two-step treatment regimen, beginning with neoadjuvant metformin+venetoclax to induce apoptosis and followed by adjuvant metformin+venetoclax+anti-PD-1 treatment to overcome immune escape, led to durable antitumor responses even after drug withdrawal. We demonstrate that pharmacological reactivation of MYC-dependent apoptosis is a powerful antitumor strategy involving both tumor cell depletion and immunosurveillance.
Conflict of interest statement
The in vivo work was partly funded by AbbVie Inc. J.D.L. is an employee and a shareholder in AbbVie Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Bieche I, et al. Quantitation of MYC gene expression in sporadic breast tumors with a real-time reverse transcription-PCR assay. Cancer Res. 1999;59:2759–2765. - PubMed
-
- Naidu R, Wahab NA, Yadav M, Kutty MK. Protein expression and molecular analysis of c-myc gene in primary breast carcinomas using immunohistochemistry and differential polymerase chain reaction. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2002;9:189–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

