Therapeutic modulation of autophagy: which disease comes first?
- PMID: 30728461
- PMCID: PMC6460393
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-019-0290-0
Therapeutic modulation of autophagy: which disease comes first?
Abstract
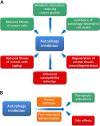
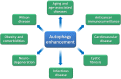
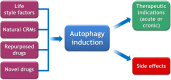
The relentless efforts of thousands of researchers have allowed deciphering the molecular machinery that regulates and executes autophagy, thus identifying multiple molecular targets to enhance or block the process, rendering autophagy "druggable". Autophagy inhibition may be useful for preserving the life of cells that otherwise would succumb to excessive self-digestion. Moreover, autophagy blockade may reduce the fitness of cancer cells or interrupt metabolic circuitries required for their growth. Autophagy stimulation is probably useful for the prevention or treatment of aging, cancer (when stimulation of immunosurveillance is the therapeutic goal), cardiovascular disease, cystic fibrosis, infection by intracellular pathogens, obesity, and intoxication by heavy metals, just to mention a few examples. Epidemiological evidence suggests broad health-improving effects for lifestyles, micronutrients, and drugs that favor autophagy. In this review, we discuss the role of autophagy in disease pathogenesis while focusing on the question, which disease will become the first clinically approved indication for therapeutic autophagy modulation.
Conflict of interest statement
GK is one of the scientific co-founders of Samsara Therapeutics. MCM declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

