MINA-1 and WAGO-4 are part of regulatory network coordinating germ cell death and RNAi in C. elegans
- PMID: 30728462
- PMCID: PMC6748153
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-019-0291-z
MINA-1 and WAGO-4 are part of regulatory network coordinating germ cell death and RNAi in C. elegans
Abstract
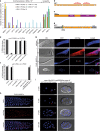
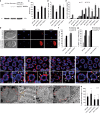
Post-transcriptional control of mRNAs by RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) has a prominent role in the regulation of gene expression. RBPs interact with mRNAs to control their biogenesis, splicing, transport, localization, translation, and stability. Defects in such regulation can lead to a wide range of human diseases from neurological disorders to cancer. Many RBPs are conserved between Caenorhabditis elegans and humans, and several are known to regulate apoptosis in the adult C. elegans germ line. How these RBPs control apoptosis is, however, largely unknown. Here, we identify mina-1(C41G7.3) in a RNA interference-based screen as a novel regulator of apoptosis, which is exclusively expressed in the adult germ line. The absence of MINA-1 causes a dramatic increase in germ cell apoptosis, a reduction in brood size, and an impaired P granules organization and structure. In vivo crosslinking immunoprecipitation experiments revealed that MINA-1 binds a set of mRNAs coding for RBPs associated with germ cell development. Additionally, a system-wide analysis of a mina-1 deletion mutant compared with wild type, including quantitative proteome and transcriptome data, hints to a post-transcriptional regulatory RBP network driven by MINA-1 during germ cell development in C. elegans. In particular, we found that the germline-specific Argonaute WAGO-4 protein levels are increased in mina-1 mutant background. Phenotypic analysis of double mutant mina-1;wago-4 revealed that contemporary loss of MINA-1 and WAGO-4 strongly rescues the phenotypes observed in mina-1 mutant background. To strengthen this functional interaction, we found that upregulation of WAGO-4 in mina-1 mutant animals causes hypersensitivity to exogenous RNAi. Our comprehensive experimental approach allowed us to describe a phenocritical interaction between two RBPs controlling germ cell apoptosis and exogenous RNAi. These findings broaden our understanding of how RBPs can orchestrate different cellular events such as differentiation and death in C. elegans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Spatiotemporal regulation of liquid-like condensates in epigenetic inheritance.Nature. 2018 May;557(7707):679-683. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0132-0. Epub 2018 May 16. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29769721 Free PMC article.
-
Widespread roles for piRNAs and WAGO-class siRNAs in shaping the germline transcriptome of Caenorhabditis elegans.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Feb 28;48(4):1811-1827. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz1178. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31872227 Free PMC article.
-
A Cytoplasmic Argonaute Protein Promotes the Inheritance of RNAi.Cell Rep. 2018 May 22;23(8):2482-2494. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.04.072. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29791857
-
RNA-binding proteins.WormBook. 2006 Apr 18:1-13. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.79.1. WormBook. 2006. PMID: 18050487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A multitasking Argonaute: exploring the many facets of C. elegans CSR-1.Chromosome Res. 2013 Dec;21(6-7):573-86. doi: 10.1007/s10577-013-9383-7. Chromosome Res. 2013. PMID: 24178449 Review.
Cited by
-
SIN-3 acts in distinct complexes to regulate the germline transcriptional program in Caenorhabditis elegans.Development. 2023 Nov 1;150(21):dev201755. doi: 10.1242/dev.201755. Epub 2023 Oct 17. Development. 2023. PMID: 37818613 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of germ cell survival and plasticity in Caenorhabditis elegans.Biochem Soc Trans. 2022 Oct 31;50(5):1517-1526. doi: 10.1042/BST20220878. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022. PMID: 36196981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel LOTUS-domain proteins are organizational hubs that recruit C. elegans Vasa to germ granules.Elife. 2021 Jul 5;10:e60833. doi: 10.7554/eLife.60833. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34223818 Free PMC article.
-
Germ granules and gene regulation in the Caenorhabditis elegans germline.Genetics. 2022 Mar 3;220(3):iyab195. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab195. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 35239965 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

