Stem Cells and Cellular Origins of Mammary Gland: Updates in Rationale, Controversies, and Cancer Relevance
- PMID: 30728840
- PMCID: PMC6341275
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/4247168
Stem Cells and Cellular Origins of Mammary Gland: Updates in Rationale, Controversies, and Cancer Relevance
Abstract
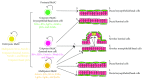
Evidences have supported the pivotal roles of stem cells in mammary gland development. Many molecular markers have been identified to characterize mammary stem cells. Cellular fate mapping of mammary stem cells by lineage tracing has put unprecedented insights into the mammary stem cell biology, which identified two subtypes of mammary stem cells, including unipotent and multipotent, which specifically differentiate to luminal or basal cells. The emerging single-cell sequencing profiles have given a more comprehensive understanding on the cellular hierarchy and lineage signatures of mammary epithelium. Besides, the stem cell niche worked as an essential regulator in sustaining the functions of mammary stem cells. In this review, we provide an overview of the characteristics of mammary stem cells. The cellular origins of mammary gland are discussed to understand the stem cell heterogeneity and their diverse differentiations. Importantly, current studies suggested that the breast cancer stem cells may originate from the mammary stem cells after specific mutations, indicating their close relationships. Here, we also outline the recent advances and controversies in the cancer relevance of mammary stem cells.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

