Detection of Pathogenic Germline Variants Among Patients With Advanced Colorectal Cancer Undergoing Tumor Genomic Profiling for Precision Medicine
- PMID: 30730459
- PMCID: PMC6415928
- DOI: 10.1097/DCR.0000000000001322
Detection of Pathogenic Germline Variants Among Patients With Advanced Colorectal Cancer Undergoing Tumor Genomic Profiling for Precision Medicine
Abstract
Background: Genomic profiling of colorectal cancer aims to identify actionable somatic mutations but can also discover incidental germline findings.
Objective: The purpose of this study was to report the detection of pathogenic germline variants that confer heritable cancer predisposition.
Design: This was a retrospective study.
Settings: The study was conducted at a tertiary-referral institution.
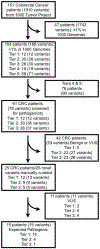
Patients: Between 2012 and 2015, 1000 patients with advanced cancer underwent targeted exome sequencing of a 202-gene panel. The subgroup of 151 patients with advanced colorectal cancer who underwent matched tumor-normal (blood) sequencing formed our study cohort.
Interventions: Germline variants in 46 genes associated with hereditary cancer predisposition were classified according to a defined algorithm based on in silico predictions of pathogenicity. Patients with presumed pathogenic variants were examined for type of mutation, as well as clinical, pedigree, and clinical genetic testing data.
Main outcome measures: We measured detection of pathogenic germline variants.
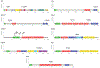
Results: A total of 1910 distinct germline variants were observed in 151 patients. After filtering, 15 pathogenic germline variants (9.9%) were found in 15 patients, arising from 9 genes of varying penetrance for colorectal cancer (APC (n = 2; 13%), ATM (n = 1; 6%), BRCA1 (n = 2; 13%), CDH1 (n = 2; 13%), CHEK2 (n = 4; 27%), MSH2 (n = 1; 7%), MSH6 (n = 1; 7%), NF2 (n = 1; 7%), and TP53 (n = 1; 7%)). Patients with pathogenic variants were diagnosed at a younger age than those without (median, 45 vs 52 y; p = 0.03). Of the 15 patients, 7 patients (46.7%) with variants in low/moderate- penetrant genes for colorectal cancer would likely have not been tested based on clinical and pedigree criteria, where 2 harbored clinically actionable variants (CDH1 and NF2, 28.5% of 7).
Limitations: This study was limited by its small sample size and advanced-stage patients.
Conclusions: Tumor-normal sequencing can incidentally discover clinically unsuspected germline variants that confer cancer predisposition in 9.9% of patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Precision medicine should integrate clinical cancer genetics to inform and interpret the actionability of germline variants and to provide follow-up care to mutation carriers. See Video Abstract at http://links.lww.com/DCR/A906.
Figures

References
-
- Kalia SS, Adelman K, Bale SJ, et al. Recommendations for reporting of secondary findings in clinical exome and genome sequencing, 2016 update (ACMG SF v2.0): a policy statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. Genet Med. 2017;19:249–255. - PubMed
-
- Robson ME, Bradbury AR, Arun B, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology Policy Statement Update: genetic and genomic testing for cancer susceptibility. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:3660–3667. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

