Effect of an interactive voice response system on self-management in kidney transplant recipients: Protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 30732143
- PMCID: PMC6380874
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014291
Effect of an interactive voice response system on self-management in kidney transplant recipients: Protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Introduction: Adherence to a complex and ongoing set of therapeutic recommendations significantly determines short and long-term outcomes after kidney transplantation (KT). Interactive voice response system (IVRS) is a novel phone-based platform which is potentially useful to deliver health behavior interventions.
Objective: The aims of the study is to describe the development of a theory-driven and educational IVRS investigate the effect of an IVRS on the self-management outcomes in KT recipients as compared with the control group.
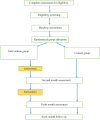
Methods: This study has been designed as a randomized, 2 parallel groups controlled trial. The KT recipients' older than18 years of age with access to a cellphone will be included. A total of 120 patients will be randomly assigned to the control and intervention groups. The participants in the intervention group will receive completely automatic calls in 3 categories: educational, medication adherence, and reminders by the IVRS, whereas those in the control group will receive usual care. The follow up will be performed within 6 months. The primary outcome will be the medication adherence while patients' transplant knowledge, health-related quality of life, and rehospitalization rates will be considered as secondary outcomes.
Results: Thus far, recruitment of participants has not been completed and results will be published in 2019.
Discussion: The IVRS is potentially useful to help KT recipients improve the self-management outcomes. The hypothesis is using an IVRS intervention makes a significant difference between basel assessment of adherence to immunosuppressive medications scale, 12-item short form survey, second version, kidney transplant understanding tool baseline scores, and those obtained at the end of study.
Trial registration number: This trial is registered with the Iran Trial Registrar under registration number IRCT20180124038492N1 and registration date 30 January 2018. https://irct.ir/trial/29215.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Jamieson NJ, Hanson CS, Josephson MA, et al. Motivations, challenges, and attitudes to self-management in kidney transplant recipients: a systematic review of qualitative studies. Am J Kidney Dis 2016;67:461–78. - PubMed
-
- Low JK, Williams A, Manias E, et al. Interventions to improve medication adherence in adult kidney transplant recipients: a systematic review. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2014;30:752–61. - PubMed
-
- Pinsky B, Takemoto SK, Lentine KL, et al. Transplant outcomes and economic costs associated with patient noncompliance to immunosuppression. Am J Transplant 2009;9:2597–606. - PubMed
-
- Andersson C. Comparison of WEB and interactive voice response (IVR) methods for delivering brief alcohol interventions to hazardous-drinking university students: a randomized controlled trial. Eur Addict Res 2015;21:240–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases