Efficacy of Mass Azithromycin Distribution for Reducing Childhood Mortality Across Geographic Regions
- PMID: 30734695
- PMCID: PMC7470520
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.18-1003
Efficacy of Mass Azithromycin Distribution for Reducing Childhood Mortality Across Geographic Regions
Abstract
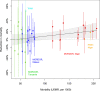
Mass azithromycin distribution has been shown to reduce all-cause mortality in preschool children in sub-Saharan Africa. However, substantial heterogeneity in the apparent effect has been noted across geographic settings, suggesting a greater relative benefit in higher mortality settings. Here, we evaluated the relationship between the underlying mortality rate and the efficacy of azithromycin for the prevention of child mortality using data from multiple sites in Ethiopia, Malawi, Niger, and Tanzania. Between regions, we find no strong evidence of effect modification of the efficacy of azithromycin distribution for the prevention of child mortality by the underlying mortality rate (P = 0.12), although a modest effect is consistent with our findings. Higher mortality settings could be prioritized, however, because of the larger number of deaths which could be averted with azithromycin distribution.
Figures
References
-
- Porco TC, et al. 2009. Effect of mass distribution of azithromycin for trachoma control on overall mortality in Ethiopian children: a randomized trial. JAMA 302: 962–968. - PubMed
-
- O’Brien KS, Emerson P, Hooper PJ, Reingold AL, Dennis EG, Keenan JD, Lietman TM, Oldenburg CE, 2019. Antimicrobial resistance following mass azithromycin distribution for trachoma: a systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis 19: e14–e25. - PubMed

