The genetic requirements of fatty acid import by Mycobacterium tuberculosis within macrophages
- PMID: 30735132
- PMCID: PMC6368401
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.43621
The genetic requirements of fatty acid import by Mycobacterium tuberculosis within macrophages
Abstract
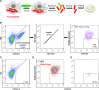
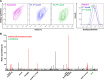
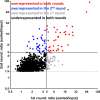
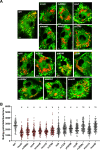
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) imports and metabolizes fatty acids to maintain infection within human macrophages. Although this is a well-established paradigm, the bacterial factors required for fatty acid import are poorly understood. Previously, we found that LucA and Mce1 are required for fatty acid import in Mtb (Nazarova et al., 2017). Here, we identified additional Mtb mutants that have a reduced ability to import a fluorescent fatty acid substrate during infection within macrophages. This screen identified the novel genes as rv2799 and rv0966c as be necessary for fatty acid import and confirmed the central role for Rv3723/LucA and putative components of the Mce1 fatty acid transporter (Rv0200/OmamB, Rv0172/Mce1D, and Rv0655/MceG) in this process.
Keywords: LucA; Mce1; Mycobacterium tuberculosis; fatty acids; infectious disease; macrophages; microbiology; tuberculosis.
© 2019, Nazarova et al.
Conflict of interest statement
EN, CM, LH, TL, DR, BV No competing interests declared
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

