No evidence of involvement of E-cadherin in cell fate specification or the segregation of Epi and PrE in mouse blastocysts
- PMID: 30735538
- PMCID: PMC6368326
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212109
No evidence of involvement of E-cadherin in cell fate specification or the segregation of Epi and PrE in mouse blastocysts
Abstract
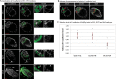
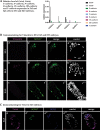
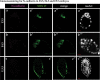
During preimplantation mouse development stages, emerging pluripotent epiblast (Epi) and extraembryonic primitive endoderm (PrE) cells are first distributed in the blastocyst in a "salt-and-pepper" manner before they segregate into separate layers. As a result of segregation, PrE cells become localised on the surface of the inner cell mass (ICM), and the Epi is enclosed by the PrE on one side and by the trophectoderm on the other. During later development, a subpopulation of PrE cells migrates away from the ICM and forms the parietal endoderm (PE), while cells remaining in contact with the Epi form the visceral endoderm (VE). Here, we asked: what are the mechanisms mediating Epi and PrE cell segregation and the subsequent VE vs PE specification? Differences in cell adhesion have been proposed; however, we demonstrate that the levels of plasma membrane-bound E-cadherin (CDH1, cadherin 1) in Epi and PrE cells only differ after the segregation of these lineages within the ICM. Moreover, manipulating E-cadherin levels did not affect lineage specification or segregation, thus failing to confirm its role during these processes. Rather, we report changes in E-cadherin localisation during later PrE-to-PE transition which are accompanied by the presence of Vimentin and Twist, supporting the hypothesis that an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition process occurs in the mouse peri-implantation blastocyst.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Journey of the mouse primitive endoderm: from specification to maturation.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022 Dec 5;377(1865):20210252. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2021.0252. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36252215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lineage segregation in human pre-implantation embryos is specified by YAP1 and TEAD1.Hum Reprod. 2023 Aug 1;38(8):1484-1498. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dead107. Hum Reprod. 2023. PMID: 37295962
-
Does mouse embryo primordial germ cell activation start before implantation as suggested by single-cell transcriptomics dynamics?Mol Hum Reprod. 2016 Mar;22(3):208-25. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gav072. Epub 2016 Jan 5. Mol Hum Reprod. 2016. PMID: 26740066
-
Cell lineage allocation within the inner cell mass of the mouse blastocyst.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2012;55:185-202. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-30406-4_10. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2012. PMID: 22918807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FGF signal-dependent segregation of primitive endoderm and epiblast in the mouse blastocyst.Development. 2010 Mar;137(5):715-24. doi: 10.1242/dev.043471. Development. 2010. PMID: 20147376
Cited by
-
ECM-integrin signalling instructs cellular position sensing to pattern the early mouse embryo.Development. 2022 Jan 1;149(1):dev200140. doi: 10.1242/dev.200140. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Development. 2022. PMID: 34908109 Free PMC article.
-
Cell fate clusters in ICM organoids arise from cell fate heredity and division: a modelling approach.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 29;10(1):22405. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80141-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33376253 Free PMC article.
-
Journey of the mouse primitive endoderm: from specification to maturation.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022 Dec 5;377(1865):20210252. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2021.0252. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36252215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analyzing embryo dormancy at single-cell resolution reveals dynamic transcriptional responses and activation of integrin-Yap/Taz prosurvival signaling.Cell Stem Cell. 2024 Sep 5;31(9):1262-1279.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2024.06.015. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Cell Stem Cell. 2024. PMID: 39047740 Free PMC article.
-
Early developmental plasticity enables the induction of an intermediate extraembryonic cell state.Sci Adv. 2022 Nov 4;8(44):eabl9583. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abl9583. Epub 2022 Nov 4. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36332016 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schrode N, Xenopoulos P, Piliszek A, Frankenberg S, Plusa B, Hadjantonakis A-K. Anatomy of a blastocyst: cell behaviors driving cell fate choice and morphogenesis in the early mouse embryo. Genes N Y N 2000 [Internet]. 2013. April [cited 2015 Jun 23];51(4):219–33. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3633705/ - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

