Using N-doped Carbon Dots Prepared Rapidly by Microwave Digestion as Nanoprobes and Nanocatalysts for Fluorescence Determination of Ultratrace Isocarbophos with Label-Free Aptamers
- PMID: 30736465
- PMCID: PMC6409902
- DOI: 10.3390/nano9020223
Using N-doped Carbon Dots Prepared Rapidly by Microwave Digestion as Nanoprobes and Nanocatalysts for Fluorescence Determination of Ultratrace Isocarbophos with Label-Free Aptamers
Abstract
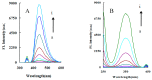
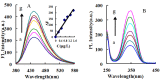
The strongly fluorescent and highly catalytic N-doped carbon dots (CDN) were rapidly prepared by a microwave irradiation procedure and were characterized by electron microscopy (EM), laser scattering, infrared spectroscopy (IR), and by their fluorescence spectrum. It was found that the CDN had a strong catalytic effect on the fluorescence reaction of 3,3',5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine hydroxide ((TMB)⁻H₂O₂) which produced the oxidation product of TMB (TMBOX) with strong fluorescence at 406 nm. The aptamer (Apt) was adsorbed on the CDN surfaces which weakened the fluorescence intensity due to the inhibition of catalytic activity. When the target molecule isocarbophos (IPS) was added, it reacted with the Apt to form a stable conjugate and free CDN which restored the catalytic activity to enhance the fluorescence. Using TMBOX as a fluorescent probe, a highly sensitive nanocatalytic method for determination of 0.025⁻1.5 μg/L IPS was established with a detection limit of 0.015 μg/L. Coupling the CDN fluorescent probe with the Apt⁻IPS reaction, a new CD fluorescence method was established for the simple and rapid determination of 0.25⁻1.5 μg/L IPS with a detection limit of 0.11 μg/L.
Keywords: TMB; aptamer; carbon dot catalysis; fluorescence; isocarbophos.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Huang R.R., Xi Z.J., He N.Y. Applications of aptamers for chemistry analysis, medicine and food security. Sci. Chi. Chem. 2015;58:1122–1130. doi: 10.1007/s11426-015-5344-7. - DOI
-
- Mahin S., Taghdisib S.M., Ansaric N., Langroodia F.A., Abnousd K., Ramezanie M. Aptamer based biosensors for detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Sens. Actuators B. 2017;241:619–635.
-
- Zhong D.L., Li Y.F., Jian L., Cheng Z.H. A Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Light-Scattering Assay of Mercury (II) on the Basis of Hg2+−DNA Complex Induced Aggregation of Gold Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009;43:5022–5027. - PubMed
-
- Du G.S., Zhang D.W., Xia B., Xu L.R., Wu S.J., Zhan S.S., Ni X., Zhou X.T., Wang L.M. A label-free colorimetric progesterone aptasensor based on the aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta. 2016;183:2251–2258. doi: 10.1007/s00604-016-1861-0. - DOI
-
- Ma L., Wen G.Q., Liu Q.Y., Liang A.H., Jiang Z.L. Resonance Rayleigh scattering determination of trace tobramycin using aptamer-modified nanogold as probe. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 2014;34:2481–2484. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

