Diagnosis in a Preclinical Model of Bladder Pain Syndrome Using a Au/ZnO Nanorod-based SERS Substrate
- PMID: 30736472
- PMCID: PMC6409757
- DOI: 10.3390/nano9020224
Diagnosis in a Preclinical Model of Bladder Pain Syndrome Using a Au/ZnO Nanorod-based SERS Substrate
Abstract
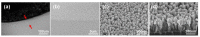
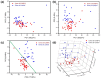
To evaluate the feasibility of ZnO nanorod-based surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) diagnostics for disease models, particularly for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS), ZnO-based SERS sensing chips were developed and applied to an animal disease model. ZnO nanorods were grown to form nano-sized porous structures and coated with gold to facilitate size-selective biomarker detection. Raman spectra were acquired on a surface enhanced Raman substrate from the urine in a rat model of IC/BPS and analyzed using a statistical analysis method called principal component analysis (PCA). The nanorods grown after the ZnO seed deposition were 30 to 50 nm in diameter and 500 to 600 nm in length. A volume of gold corresponding to a thin film thickness of 100 nm was deposited on the grown nanorod structure. Raman spectroscopic signals were measured in the scattered region for nanometer biomarker detection to indicate IC/BPS. The Raman peaks for the control group and IC/BPS group are observed at 641, 683, 723, 873, 1002, 1030, and 1355 cm-1, which corresponded to various bonding types and compounds. The PCA results are plotted in 2D and 3D. The Raman signals and statistical analyses obtained from the nano-sized biomarkers of intractable inflammatory diseases demonstrate the possibility of an early diagnosis.
Keywords: ZnO nanorods; interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS); principal component analysis (PCA); surface enhancement Raman spectroscopy (SERS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Selective Detection of Nano-Sized Diagnostic Markers Using Au-ZnO Nanorod-Based Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) in Ureteral Obstruction Models.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Oct 22;15:8121-8130. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S272500. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33122904 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of ZnO Nanorod-Based Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering Substrates for Bio-Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019 Mar 17;9(3):447. doi: 10.3390/nano9030447. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30884889 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of local surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) effect by biocompatible metal clustering based on ZnO nanorods in Raman measurements.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2018 Nov 5;204:203-208. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2018.06.045. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2018. PMID: 29935391
-
SERS Effect on Spin-Coated Seeding of Tilted Au-ZnO Nanorods for Low-Cost Diagnosis.Materials (Basel). 2020 Nov 24;13(23):5321. doi: 10.3390/ma13235321. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33255438 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Effect Enhanced Raman Scattering Based on Au/ZnO Nanorods Structures.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Oct 27;12(21):3785. doi: 10.3390/nano12213785. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36364559 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Label-free atherosclerosis diagnosis through a blood drop of apolipoprotein E knockout mouse model using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy validated by machine learning algorithm.Bioeng Transl Med. 2023 May 3;8(4):e10529. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10529. eCollection 2023 Jul. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37476064 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Detection of Nano-Sized Diagnostic Markers Using Au-ZnO Nanorod-Based Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) in Ureteral Obstruction Models.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Oct 22;15:8121-8130. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S272500. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33122904 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kikuchi H., Kawabata T., Okazaki S., Hiramatsu Y., Baba M., Ohta M., Kamiya K., Tanaka T., Konno H. Near-infrared multichannel Raman spectroscopy with a 1064-nm excitation wavelength for ex vivo diagnosis of gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 2011;71:e137–e143. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.Am2011-5312. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

