Developing an Enzyme-Assisted Derivatization Method for Analysis of C27 Bile Alcohols and Acids by Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 30736477
- PMCID: PMC6384595
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24030597
Developing an Enzyme-Assisted Derivatization Method for Analysis of C27 Bile Alcohols and Acids by Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
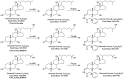
Enzyme-assisted derivatization for sterol analysis (EADSA) is a technology designed to enhance sensitivity and specificity for sterol analysis using electrospray ionization⁻mass spectrometry. To date it has only been exploited on sterols with a 3β-hydroxy-5-ene or 3β-hydroxy-5α-hydrogen structure, using bacterial cholesterol oxidase enzyme to convert the 3β-hydroxy group to a 3-oxo group for subsequent derivatization with the positively charged Girard hydrazine reagents, or on substrates with a native oxo group. Here we describe an extension of the technology by substituting 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3α-HSD) for cholesterol oxidase, making the method applicable to sterols with a 3α-hydroxy-5β-hydrogen structure. The 3α-HSD enzyme works efficiently on bile alcohols and bile acids with this stereochemistry. However, as found by others, derivatization of the resultant 3-oxo group with a hydrazine reagent does not go to completion in the absence of a conjugating double bond in the sterol structure. Nevertheless, Girard P derivatives of bile alcohols and C27 acids give an intense molecular ion ([M]⁺) upon electrospray ionization and informative fragmentation spectra. The method shows promise for analysis of bile alcohols and 3α-hydroxy-5β-C27-acids, enhancing the range of sterols that can be analyzed at high sensitivity in sterolomic studies.
Keywords: Girard reagent; bile alcohol; cholestanoic acid; electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry; enzyme-assisted derivatization; oxysterol; sterolomics.
Conflict of interest statement
W.J.G., P.J.C. and Y.W. are listed as inventors on the patent “Kit and method for quantitative detection of steroids” US9851368B2. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Novel, major 2α- and 2β-hydroxy bile alcohols and bile acids in the bile of Arapaima gigas, a large South American river fish.Steroids. 2016 Mar;107:112-20. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2016.01.001. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Steroids. 2016. PMID: 26768415
-
Rapid identification of bile acids in snake bile using ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016 Nov 15;1036-1037:157-169. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.10.011. Epub 2016 Oct 11. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27760405
-
Biliary bile acids, bile alcohols, and sterols of Alligator mississippiensis.J Lipid Res. 1980 Jan;21(1):110-7. J Lipid Res. 1980. PMID: 7354247
-
Bile acids: analysis in biological fluids and tissues.J Lipid Res. 2010 Jan;51(1):23-41. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R001941-JLR200. J Lipid Res. 2010. PMID: 20008121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Infant with 3β-hydroxy-Δ(5)-C27 steroid dehydrogenase deficiency: report of two cases and literatures review].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2015 May;53(5):360-5. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26080666 Review. Chinese.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

