A case report of community-acquired Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia complicated with MODS in a previously healthy patient and related literature review
- PMID: 30736735
- PMCID: PMC6368713
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-019-3765-1
A case report of community-acquired Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia complicated with MODS in a previously healthy patient and related literature review
Abstract
Background: Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an unusual pathogen in community-acquired pneumonia, especially in previously healthy adults, but often indicates poor prognosis.
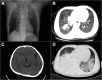
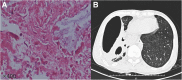
Case presentation: We report a previously healthy patient who developed severe community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) caused by P. aeruginosa. He deteriorated to septic shock and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) quickly, complicated by secondary hematogenous central nervous system (CNS) infection. After 1 month of organ support and antipseudomonal therapy, he had significant symptomatic improvement and was discharged from hospital. During treatment, the pathogen developed resistance to carbapenems quickly and the antibiotic regimen was adjusted accordingly.
Conclusions: According to our case and related literature review, we conclude that more attention should be paid to community-acquired Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia, because of its rapid progression and poor prognosis.
Keywords: CAP; MODS; Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not Required.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Frankel E. Investigations about the pathogenicity of the human Bacillus pyocyaneus [in German] Z Hyg Infekt. 1917;84:369–423. doi: 10.1007/BF02284438. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

