A mapping review of research on gambling harm in three regulatory environments
- PMID: 30736817
- PMCID: PMC6368783
- DOI: 10.1186/s12954-018-0265-3
A mapping review of research on gambling harm in three regulatory environments
Abstract
Background: Harmful gambling is a complex issue with diverse antecedents and resulting harms that have been studied from multiple disciplinary perspectives. Although previous bibliometric reviews of gambling studies have found a dominance of judgement and decision-making research, no bibliometric review has examined the concept of "harm" in the gambling literature, and little work has quantitatively assessed how gambling research priorities differ between countries.
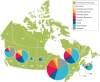
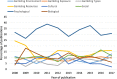
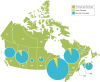
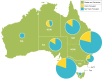
Methods: Guided by the Conceptual Framework of Harmful Gambling (CFHG), an internationally relevant framework of antecedents to harmful gambling, we conducted a bibliometric analysis focusing on research outputs from three countries with different gambling regulatory environments: Canada, Australia, and New Zealand. Using a Web of Science database search, 1424 articles published from 2008 to 2017 were retrieved that could be mapped to the eight CFHG factors. A subsample of articles (n = 171) containing the word "harm" in the title, abstract, or keywords was then drawn. Descriptive statistics were used to examine differences between countries and trends over time with regard to CFHG factor and harm focus.
Results: Psychological and biological factors dominate gambling research in Canada whereas resources and treatment have received more attention in New Zealand. A greater percentage of Australia and New Zealand publications address the gambling environment and exposure to gambling than in Canada. The subset of articles focused on harm showed a stronger harms focus among New Zealand and Australian researchers compared to Canadian-authored publications.
Conclusions: The findings provide preliminary bibliometric evidence that gambling research foci may be shaped by jurisdictional regulation of gambling. Countries with privately operated gambling focused on harm factors that are the operators' responsibility, whereas jurisdictions with a public health model focused on treatment and harm reduction resources. In the absence of a legislated requirement for public health or harm minimisation focus, researchers in jurisdictions with government-operated gambling tend to focus research on factors that are the individual's responsibility and less on the harms they experience. Given increased international attention to gambling-related harm, regulatory and research environments could promote and support more diverse research in this area.
Keywords: Australia; Bibliometric analysis; Canada; Conceptual Framework of Harmful Gambling; Gambling harm; Mapping review; New Zealand.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




References
-
- Rinia EJ, Van Leeuwen TN, EEW B, Van Vuren HG, AFJ VR. Citation delay in interdisciplinary knowledge exchange. Scientometrics. 2001;51:293–309. doi: 10.1023/A:1010589300829. - DOI
-
- Yan E. Disciplinary knowledge production and diffusion in science. J Assoc Inf Sci Technol. 2016;67:2223–2245. doi: 10.1002/asi.23541. - DOI
-
- Abbott M, Binde P, Clark L, Hodgins D, Pereira A, Quilty L, Thomas A, Volberg R, Walker D, Williams RJ. Conceptual Framework of Harmful Gambling: An international collaboration (Rev. Ed.). Guelph, ON: Gambling Research Exchange Ontario; 2015. [http://www.greo.ca/Modules/EvidenceCentre/Details/conceptual-framework-o...].
-
- Ferris J, Wynne H. The Canadian Problem Gambling Index. Ottawa, ON: Canadian Centre on Substance Abuse; 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

