Clonal Deletion of Tumor-Specific T Cells by Interferon-γ Confers Therapeutic Resistance to Combination Immune Checkpoint Blockade
- PMID: 30737146
- PMCID: PMC6886475
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.01.006
Clonal Deletion of Tumor-Specific T Cells by Interferon-γ Confers Therapeutic Resistance to Combination Immune Checkpoint Blockade
Abstract
Resistance to checkpoint-blockade treatments is a challenge in the clinic. We found that although treatment with combined anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 improved control of established tumors, this combination compromised anti-tumor immunity in the low tumor burden (LTB) state in pre-clinical models as well as in melanoma patients. Activated tumor-specific T cells expressed higher amounts of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) receptor and were more susceptible to apoptosis than naive T cells. Combination treatment induced deletion of tumor-specific T cells and altered the T cell repertoire landscape, skewing the distribution of T cells toward lower-frequency clonotypes. Additionally, combination therapy induced higher IFN-γ production in the LTB state than in the high tumor burden (HTB) state on a per-cell basis, reflecting a less exhausted immune status in the LTB state. Thus, elevated IFN-γ secretion in the LTB state contributes to the development of an immune-intrinsic mechanism of resistance to combination checkpoint blockade, highlighting the importance of achieving the optimal magnitude of immune stimulation for successful combination immunotherapy strategies.
Keywords: IFN-γ; activation-induced cell death; anti-CTLA-4; anti-PD-1; cancer; immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


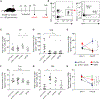
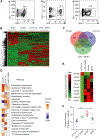


Comment in
-
Live or Let Die: T Cell Survival in Cancer Immunotherapy.Immunity. 2019 Feb 19;50(2):280-282. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.01.016. Immunity. 2019. PMID: 30784574
References
-
- Badovinac VP, Tvinnereim AR, and Harty JT (2000). Regulation of antigen-specific CD8+ T cell homeostasis by perforin and interferon-gamma. Science 290, 1354–1358. - PubMed
-
- Berner V, Liu H, Zhou Q, Alderson KL, Sun K, Weiss JM, Back TC, Longo DL, Blazar BR, Wiltrout RH, et al. (2007). IFN-gamma mediates CD4+ T-cell loss and impairs secondary antitumor responses after successful initial immunotherapy. Nat. Med. 13, 354–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

