Clinical spectrum of STX1B-related epileptic disorders
- PMID: 30737342
- PMCID: PMC6511102
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007089
Clinical spectrum of STX1B-related epileptic disorders
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to expand the spectrum of epilepsy syndromes related to STX1B, encoding the presynaptic protein syntaxin-1B, and establish genotype-phenotype correlations by identifying further disease-related variants.
Methods: We used next-generation sequencing in the framework of research projects and diagnostic testing. Clinical data and EEGs were reviewed, including already published cases. To estimate the pathogenicity of the variants, we used established and newly developed in silico prediction tools.
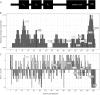
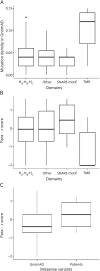
Results: We describe 17 new variants in STX1B, which are distributed across the whole gene. We discerned 4 different phenotypic groups across the newly identified and previously published patients (49 patients in 23 families): (1) 6 sporadic patients or families (31 affected individuals) with febrile and afebrile seizures with a benign course, generally good drug response, normal development, and without permanent neurologic deficits; (2) 2 patients with genetic generalized epilepsy without febrile seizures and cognitive deficits; (3) 13 patients or families with intractable seizures, developmental regression after seizure onset and additional neuropsychiatric symptoms; (4) 2 patients with focal epilepsy. More often, we found loss-of-function mutations in benign syndromes, whereas missense variants in the SNARE motif of syntaxin-1B were associated with more severe phenotypes.
Conclusion: These data expand the genetic and phenotypic spectrum of STX1B-related epilepsies to a diverse range of epilepsies that span the International League Against Epilepsy classification. Variants in STX1B are protean and contribute to many different epilepsy phenotypes, similar to SCN1A, the most important gene associated with fever-associated epilepsies.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures

References
-
- Cossette P, Liu L, Brisebois K, et al. . Mutation of GABRA1 in an autosomal dominant form of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Nat Genet 2002;31:184–189. - PubMed
-
- Striano P, Weber YG, Toliat MR, et al. . GLUT1 mutations are a rare cause of familial idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Neurology 2012;78:557–562. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Lu J, Pan H, et al. . Association between genetic variation of CACNA1H and childhood absence epilepsy. Ann Neurol 2003;54:239–243. - PubMed
-
- Scheffer IE, Berkovic SF. Generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus: a genetic disorder with heterogeneous clinical phenotypes. Brain 1997;120:479–490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
