Alkali treated antioxidative crude polysaccharide from Russula alatoreticula potentiates murine macrophages by tunning TLR/NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 30737411
- PMCID: PMC6368593
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-37998-2
Alkali treated antioxidative crude polysaccharide from Russula alatoreticula potentiates murine macrophages by tunning TLR/NF-κB pathway
Abstract
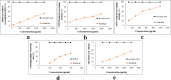
In our previous research, Russula alatoreticula was demonstrated as a novel species, ethnic myco-food and reservoir of hot water extractable polysaccharides. However, residue after the hydrothermal process still offer plenty of medicinal carbohydrates that could easily be extracted by using alkali solvent. Thus, the present work was attempted to prepare crude polysaccharide using remainder of the conventional method and subsequently a β-glucan enriched fraction, RualaCap, was isolated. The bio-polymers displayed pronounced therapeutic efficacy as evident by radical scavenging, chelating ability, reducing power and total antioxidant capacity. In addition, strong immune-enhancing potential was also observed indicated by augmentation in macrophage viability, phagocytic uptake, nitric oxide (NO) production and reactive oxygen species (ROS) synthesis. Alongside, the polysaccharides effectively triggered transcriptional activation of Toll like receptor (TLR)-2, TLR-4, nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, Iκ-Bα, interferon (IFN)-γ and interleukin (IL)-10 genes explaining mode of action. Taken together, our results signify possibility of RualaCap as a potent nutraceutical agent and enhance importance of R. alatoreticula especially in the field of innate immune stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Kodama S, et al. Subcritical water extraction of polysaccharides using a semi-batch extractor. Mod. Appl. Sci. 2015;9:220–224. doi: 10.5539/mas.v9n7p220. - DOI
-
- Ching, F. M. Chinese herbal drug research trends. (Nova Science Publishers: New York, 2007).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

