Expression of Syk and MAP4 proteins in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 30737623
- PMCID: PMC6435630
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-019-02856-9
Expression of Syk and MAP4 proteins in ovarian cancer
Abstract
Purpose: We have previously reported on the prognostic importance of the calpain family of proteins in ovarian cancer, especially calpain-2. Spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) phosphorylates a variety of cytoskeletal proteins with studies suggesting potential interactions between Syk and conventional calpains. Microtubule-associated protein 4 (MAP4) has been reported to be regulated by Syk.
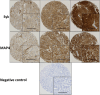
Methods: The current study assessed Syk and MAP4 protein expression, by immunohistochemistry on a tissue microarray comprised of cores from primary ovarian carcinomas (n = 575), to evaluate associations with patient clinical outcomes and other clinicopathological factors and sought to determine whether there were any correlations between the expression of Syk, MAP4 and the calpain system.
Results: MAP4 expression was significantly associated with ovarian cancer histological subtype (P < 0.001), stage (P = 0.001), grade (P < 0.001) and residual tumour (P = 0.005). Despite this finding, we found no significant association existing between MAP4 expression and overall survival. Syk expression was also found significantly associated with histological subtype (P < 0.001). Syk seems to play a contradictory role with respect to tumour progression: low cytoplasmic Syk expression was significantly associated with low stage (P = 0.013), and low nuclear Syk expression with chemo-resistance in patients treated with taxane-containing therapy (P = 0.006). Interestingly, despite the lack of association in the whole cohort, high nuclear Syk expression was significantly associated with better overall survival in certain subgroups (P = 0.001).
Conclusions: The current study indicates a lack of correlation between calpain-2 expression and Syk and MAP4. Syk, MAP4 and calpain-1 appeared to significantly correlate with each other in the whole cohort, with calpain-1 being more highly associated with MAP4 and Syk in mucinous carcinomas. Overall, the current results suggest that Syk, MAP4, and calpain-1 expression are correlated with each other and these proteins may be involved in early stages of tumour spread.
Keywords: Calpain; Calpastatin; Chemotherapy; MAP4; Ovarian cancer; Syk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Aoki D, Oda Y, Hattori S, Taguchi K, Ohishi Y, Basaki Y, Oie S, Suzuki N, Kono S, Tsuneyoshi M et al (2009) Overexpression of class III beta-tubulin predicts good response to taxane-based chemotherapy in ovarian clear cell adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 15(4):1473–1480. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1274 - PubMed
-
- Baldock D, Graham B, Akhlaq M, Graff P, Jones CE, Menear K (2000) Purification and characterization of human Syk produced using a baculovirus expression system. Protein Expr Purif 18(1):86–94 - PubMed
-
- Camp RL, Dolled-Filhart M, Rimm DL (2004) X-tile: a new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin Cancer Res 10(21):7252–7259 - PubMed
-
- Chuanliang P, Yunpeng Z, Yingtao H, Qifeng S, Xiaogang Z, Bo C (2016) Syk expression in non-small-cell lung cancer and its relation with angiogenesis. J Cancer Res Ther 12(2):663–666. 10.4103/0973-1482.154082 - PubMed
-
- Coopman PJ, Mueller SC (2006) The Syk tyrosine kinase: a new negative regulator in tumor growth and progression. Cancer Lett 241(2):159–173 (Epub 2006 Jan 27) - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

