Functionalized Phenylbenzamides Inhibit Aquaporin-4 Reducing Cerebral Edema and Improving Outcome in Two Models of CNS Injury
- PMID: 30738082
- PMCID: PMC6495193
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.01.034
Functionalized Phenylbenzamides Inhibit Aquaporin-4 Reducing Cerebral Edema and Improving Outcome in Two Models of CNS Injury
Abstract
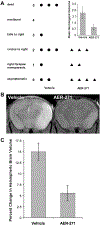
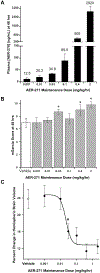
Cerebral edema in ischemic stroke can lead to increased intracranial pressure, reduced cerebral blood flow and neuronal death. Unfortunately, current therapies for cerebral edema are either ineffective or highly invasive. During the development of cytotoxic and subsequent ionic cerebral edema water enters the brain by moving across an intact blood brain barrier and through aquaporin-4 (AQP4) at astrocyte endfeet. Using AQP4-expressing cells, we screened small molecule libraries for inhibitors that reduce AQP4-mediated water permeability. Additional functional assays were used to validate AQP4 inhibition and identified a promising structural series for medicinal chemistry. These efforts improved potency and revealed a compound we designated AER-270, N-[3,5-bis (trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzamide. AER-270 and a prodrug with enhanced solubility, AER-271 2-{[3,5-Bis(trifluoromethyl) phenyl]carbamoyl}-4-chlorophenyl dihydrogen phosphate, improved neurological outcome and reduced swelling in two models of CNS injury complicated by cerebral edema: water intoxication and ischemic stroke modeled by middle cerebral artery occlusion.
Keywords: AQP4 inhibitor; MCAo; cerebral edema; cytotoxic edema; ischemic stroke; water intoxication.
Copyright © 2019 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
G.W.F., C.H.H., S.M.F., J.M.D., A.G.A., J.M.B., P.R.M., W.F.B and M.F.P. were employees of and/or received compensation from Aeromics, Inc. All other authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of phosphodiesterase 4 attenuates aquaporin 4 expression and astrocyte swelling following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.Glia. 2024 Sep;72(9):1629-1645. doi: 10.1002/glia.24572. Epub 2024 May 24. Glia. 2024. PMID: 38785370
-
Atorvastatin Pretreatment Attenuates Ischemic Brain Edema by Suppressing Aquaporin 4.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018 Nov;27(11):3247-3255. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2018.07.011. Epub 2018 Aug 6. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018. PMID: 30093197
-
AQP4-A25Q Point Mutation in Mice Depolymerizes Orthogonal Arrays of Particles and Decreases Polarized Expression of AQP4 Protein in Astrocytic Endfeet at the Blood-Brain Barrier.J Neurosci. 2022 Oct 26;42(43):8169-8183. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0401-22.2022. Epub 2022 Sep 13. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36100398 Free PMC article.
-
Role of aquaporin-4 in cerebral edema and stroke.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009;(190):159-70. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-79885-9_7. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19096776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aquaporin-4 in brain and spinal cord oedema.Neuroscience. 2010 Jul 28;168(4):1036-46. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.08.019. Epub 2009 Aug 12. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 19682555 Review.
Cited by
-
Microenvironmental Variations After Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown in Traumatic Brain Injury.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Nov 26;14:750810. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.750810. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34899180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astrocyte aquaporin mediates a tonic water efflux maintaining brain homeostasis.Elife. 2024 Nov 7;13:RP95873. doi: 10.7554/eLife.95873. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39508543 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights on Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets of Cerebral Edema.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024;22(14):2330-2352. doi: 10.2174/1570159X22666240528160237. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38808718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring Aquaporins in Human Studies: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential in Critical Illness.Life (Basel). 2024 Dec 20;14(12):1688. doi: 10.3390/life14121688. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39768394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aquaporins: New players in breast cancer progression and treatment response.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 21;12:988119. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.988119. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36212456 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amiry-Moghaddam M, Frydenlund DS, Ottersen OP (2004) Anchoring of aquaporin-4 in brain: molecular mechanisms and implications for the physiology and pathophysiology of water transport. Neuroscience 129:999–1010. - PubMed
-
- Anders JJ, Brightman MW (1979) Assemblies of particles in the cell membranes of developing, mature and reactive astrocytes. J Neurocytol 8:777–795. - PubMed
-
- Arac A, Blanchard V, Lee M, Steinberg GK (2009) Assessment of outcome following decompressive craniectomy for malignant middle cerebral artery infarction in patients older than 60 years of age. Neurosur Focus 26:E3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

