The roles of supervised machine learning in systems neuroscience
- PMID: 30738835
- PMCID: PMC8454059
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2019.01.008
The roles of supervised machine learning in systems neuroscience
Abstract
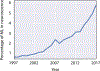
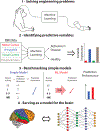
Over the last several years, the use of machine learning (ML) in neuroscience has been rapidly increasing. Here, we review ML's contributions, both realized and potential, across several areas of systems neuroscience. We describe four primary roles of ML within neuroscience: (1) creating solutions to engineering problems, (2) identifying predictive variables, (3) setting benchmarks for simple models of the brain, and (4) serving itself as a model for the brain. The breadth and ease of its applicability suggests that machine learning should be in the toolbox of most systems neuroscientists.
Keywords: Deep learning; Machine learning; Modeling; Neural activity; Neuroanatomy; Supervised learning; Systems neuroscience.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Agrawal Pulkit, Stansbury Dustin, Malik Jitendra, and Gallant Jack L. 2014. “Pixels to Voxels: Modeling Visual Representation in the Human Brain.” arXiv [q-bio.NC]. arXiv http://arxiv.org/abs/1407.5104.
-
- Anderson David J., and Perona Pietro. 2014. “Toward a Science of Computational Ethology.” Neuron 84 (1): 18–31. - PubMed
-
- Appenzeller Tim. 2017. “The AI Revolution in Science.” Science 10.1126/science.aan7064. - DOI
-
- Arakaki Takafumi, Barello G, and Ahmadian Yashar. 2017. “Capturing the Diversity of Biological Tuning Curves Using Generative Adversarial Networks.” arXiv [q-bio.QM]. arXiv http://arxiv.org/abs/1707.04582.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

