Fluorinated Aromatic Monomers as Building Blocks To Control α-Peptoid Conformation and Structure
- PMID: 30739443
- PMCID: PMC6463299
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.8b13498
Fluorinated Aromatic Monomers as Building Blocks To Control α-Peptoid Conformation and Structure
Abstract
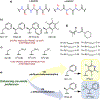
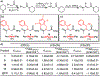
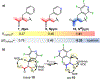
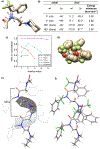
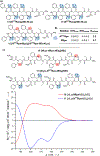
Peptoids are peptidomimetics of interest in the fields of drug development and biomaterials. However, obtaining stable secondary structures is challenging, and designing these requires effective control of the peptoid tertiary amide cis/trans equilibrium. Herein, we report new fluorine-containing aromatic monomers that can control peptoid conformation. Specifically, we demonstrate that a fluoro-pyridine group can be used to circumvent the need for monomer chirality to control the cis/trans equilibrium. We also show that incorporation of a trifluoro-methyl group ( NCF3Rpe) rather than a methyl group ( NRpe) at the α-carbon of a monomer gives rise to a 5-fold increase in cis-isomer preference.
Figures
References
-
- Sanborn TJ; Wu CW; Zuckermann RN; Barron AE Extreme stability of helices formed by water-soluble poly-N-substituted glycines (polypeptoids) with α-chiral side chains. Biopolymers 2002, 63 (1), 12–20. - PubMed
-
- Eggimann GA; Bolt HL; Denny PW; Cobb SL Investigating the Anti-leishmanial Effects of Linear Peptoids. ChemMedChem 2015, 10 (2), 233–237 - PubMed
-
- Hara T; Durell SR; Myers MC; Appella DH Probing the Structural Requirements of Peptoids That Inhibit HDM2–p53 Interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2006, 128 (6), 1995–2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

