Feasibility of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Wideband Protocol in Patients With Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators and Its Utility for Defining Scar
- PMID: 30739658
- PMCID: PMC8240651
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2019.01.018
Feasibility of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Wideband Protocol in Patients With Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators and Its Utility for Defining Scar
Abstract
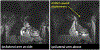
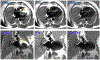
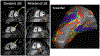
Implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) have been a relative contraindication to cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging. Although cardiovascular magnetic resonance provides valuable information regarding scar in patients with ventricular arrhythmias or cardiomyopathy, ICDs in these patients frequently cause artifacts hindering accurate interpretation of both cine and late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) images. We sought to quantify the frequency and severity of artifact on LGE images and assess whether a modified wideband LGE protocol could improve the diagnostic yield of scar identification in agreement with invasive electroanatomic mapping (EAM). Forty-nine patients with ICDs and ventricular tachycardia (VT) or cardiomyopathy underwent CMR (Philips 1.5T), including standard and wideband LGE imaging. A safety algorithm was followed throughout the protocol. Standard and wideband LGE short-axis images were graded using an artifact score on a per-slice basis. LGE on wideband images was compared with EAM in 27 of 49 patients who underwent VT ablation. There were no adverse patient- or device-related events. With standard LGE imaging, 84% of patients demonstrated some degree of hyperenhancement artifact, which persisted in 22% on wideband LGE but with much less extent. Wideband LGE imaging resulted in an increase from 48% to 94% diagnostic-quality slices, with a significant reduction in artifact score, and correlated with EAM in 21 of 27 patients (78%). In conclusion, assessment of standard LGE is markedly limited by artifact in patients with ICD. The use of wideband LGE significantly improves image quality and can accurately localize myocardial scar before VT ablation.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

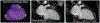
References
-
- Nazarian S, Hansford R, Roguin A, Goldsher D, Zviman MM, Lardo AC, Caffo BS, Frick KD, Kraut MA, Kamel IR, Calkins H, Berger RD, Bluemke DA, Halperin HR. A prospective evaluation of a protocol for magnetic resonance imaging of patients with implanted cardiac devices. Ann Intern Med 2011;155:415–424. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Russo RJ, Costa HS, Silva PD, Anderson JL, Arshad A, Biederman RW, Boyle NG, Frabizzio JV, Birgersdotter-Green U, Higgins SL, Lampert R, Machado CE, Martin ET, Rivard AL, Rubenstein JC, Schaerf RH, Schwartz JD, Shah DJ, Tomassoni GF, Tominaga GT, Tonkin AE, Uretsky S, Wolff SD. Assessing the risks associated with MRI in patients with a pacemaker or defibrillator. N Engl J Med 2017;376:755–764. - PubMed
-
- Naehle CP, Kreuz J, Strach K, Schwab JO, Pingel S, Luechinger R, Fimmers R, Schild H, Thomas D. Safety, feasibility, and diagnostic value of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in patients with cardiac pacemakers and implantable cardioverters/defibrillators at 1.5 T. Am Heart J 2011;161:1096–1105. - PubMed
-
- Sasaki T, Hansford R, Zviman MM, Kolandaivelu A, Bluemke DA, Berger RD, Calkins H, Halperin HR, Nazarian S. Quantitative assessment of artifacts on cardiac magnetic resonance imaging of patients with pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 2011;4:662–670. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Horwood L, Attili A, Luba F, Ibrahim EH, Parmar H, Stojanovska J, Gadoth-Goodman S, Fette C, Oral H, Bogun F. Magnetic resonance imaging in patients with cardiac implanted electronic devices: focus on contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging protocols. Europace 2017;19:812–817. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

