Resolving the Paradox of Hepatic Insulin Resistance
- PMID: 30739869
- PMCID: PMC6369222
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2018.10.016
Resolving the Paradox of Hepatic Insulin Resistance
Abstract
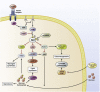
Insulin resistance is associated with numerous metabolic disorders, such as obesity and type II diabetes, that currently plague our society. Although insulin normally promotes anabolic metabolism in the liver by increasing glucose consumption and lipid synthesis, insulin-resistant individuals fail to inhibit hepatic glucose production and paradoxically have increased liver lipid synthesis, leading to hyperglycemia and hypertriglyceridemia. Here, we detail the intrahepatic and extrahepatic pathways mediating insulin's control of glucose and lipid metabolism. We propose that the interplay between both of these pathways controls insulin signaling and that mis-regulation between the 2 results in the paradoxic effects seen in the insulin-resistant liver instead of the commonly proposed deficiencies in particular branches of only the direct hepatic pathway.
Keywords: De Novo Lipogenesis; Hepatic Glucose Production; Hepatic Insulin Resistance; Insulin Signaling; Metabolism; PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Zimmet P., Alberti K.G.M.M., Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature. 2001;414:782–787. - PubMed
-
- Brown M.S., Goldstein J.L. Selective versus total insulin resistance: a pathogenic paradox. Cell Metab. 2008;7:95–96. - PubMed
-
- James O.F.W., Day C.P. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): a disease of emerging identity and importance. J Hepatol. 1998;29:495–501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

