Nanoscale Metal-Organic Frameworks for Phototherapy of Cancer
- PMID: 30739946
- PMCID: PMC6366651
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2017.09.007
Nanoscale Metal-Organic Frameworks for Phototherapy of Cancer
Abstract
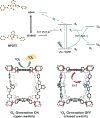
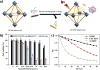
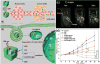
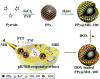
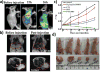
Phototherapy involves the irradiation of tissues with light, and is commonly implemented in the forms of photodynamic therapy (PDT) and photothermal therapy (PTT). Photosensitizers (PSs) are often needed to improve the efficacy and selectivity of phototherapy via enhanced singlet oxygen generation in PDT and photothermal responses in PTT. In both cases, efficient and selective delivery of PSs to the diseased tissues is of paramount importance. Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks (nMOFs), a new class of hybrid materials built from metal connecting points and bridging ligands, have been examined as nanocarriers for drug delivery due to their compositional and structural tunability, highly porous structures, and good biocompatibility. This review summarizes recent advances on using nMOFs as nanoparticle PSs for applications in PDT and PTT.
Keywords: Metal-organic framework; Nanophotosensitizers; Photodynamic therapy; Photothermal therapy.
Figures
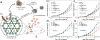
References
-
- Ackroyd R, Kelty C, Brown N, Reed M. Photochemistry and Photobiology. 2001;74:656–669. - PubMed
-
- Pushpan S, Venkatraman S, Anand V, Sankar J, Parmeswaran D, Ganesan S, Chandrashekar T. Current Medicinal Chemistry-Anti-Cancer Agents. 2002;2:187–207. - PubMed
-
- Roelandts R. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 2002;46:926–930. - PubMed
-
- Møller KI, Kongshoj B, Philipsen PA, Thomsen VO, Wulf HC. Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine. 2005;21:118–124. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
