Global Gene Knockout of Kcnip3 Enhances Pain Sensitivity and Exacerbates Negative Emotions in Rats
- PMID: 30740043
- PMCID: PMC6355686
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00005
Global Gene Knockout of Kcnip3 Enhances Pain Sensitivity and Exacerbates Negative Emotions in Rats
Abstract
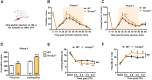
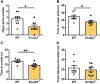
The Ca2+-binding protein Kv channel interacting protein 3 (KChIP3) or downstream regulatory element antagonist modulator (DREAM), a member of the neuronal calcium sensor (NCS) family, shows remarkable multifunctional properties. It acts as a transcriptional repressor in the nucleus and a modulator of ion channels or receptors, such as Kv4, NMDA receptors and TRPV1 channels on the cytomembrane. Previous studies of Kcnip3 -/- mice have indicated that KChIP3 facilitates pain hypersensitivity by repressing Pdyn expression in the spinal cord. Conversely, studies from transgenic daDREAM (dominant active DREAM) mice indicated that KChIP3 contributes to analgesia by repressing Bdnf expression and attenuating the development of central sensitization. To further determine the role of KChIP3 in pain transmission and its possible involvement in emotional processing, we assessed the pain sensitivity and negative emotional behaviors of Kcnip3 -/- rats. The knockout rats showed higher pain sensitivity compared to the wild-type rats both in the acute nociceptive pain model and in the late phase (i.e., 2, 4 and 6 days post complete Freund's adjuvant injection) of the chronic inflammatory pain model. Importantly, Kcnip3 -/- rats displayed stronger aversion to the pain-associated compartment, higher anxiety level and aggravated depression-like behavior. Furthermore, RNA-Seq transcriptional profiling of the forebrain cortex were compared between wild-type and Kcnip3 -/- rats. Among the 68 upregulated genes, 19 genes (including Nr4a2, Ret, Cplx3, Rgs9, and Itgad) are associated with neural development or synaptic transmission, particularly dopamine neurotransmission. Among the 79 downregulated genes, 16 genes (including Col3a1, Itm2a, Pcdhb3, Pcdhb22, Pcdhb20, Ddc, and Sncaip) are associated with neural development or dopaminergic transmission. Transcriptional upregulation of Nr4a2, Ret, Cplx3 and Rgs9, and downregulation of Col3a1, Itm2a, Pcdhb3 and Ddc, were validated by qPCR analysis. In summary, our studies showed that Kcnip3 -/- rats displayed higher pain sensitivity and stronger negative emotions, suggesting an involvement of KChIP3 in negative emotions and possible role in central nociceptive processing.
Keywords: KChIP3; RNA-Seq analysis; anxiety; conditioned place aversion; depression; inflammatory pain; negative emotions; nociceptive pain.
Figures




Similar articles
-
KChIP3 N-Terminal 31-50 Fragment Mediates Its Association with TRPV1 and Alleviates Inflammatory Hyperalgesia in Rats.J Neurosci. 2018 Feb 14;38(7):1756-1773. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2242-17.2018. Epub 2018 Jan 15. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29335353 Free PMC article.
-
Subcellular localization and transcription regulatory potency of KCNIP/Calsenilin/DREAM/KChIP proteins in cultured primary cortical neurons do not provide support for their role in CRE-dependent gene expression.J Neurochem. 2012 Oct;123(1):29-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07796.x. Epub 2012 Jun 27. J Neurochem. 2012. PMID: 22612322
-
Hyperglycemia induces early upregulation of the calcium sensor KChIP3/DREAM/calsenilin in the rat retina.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Feb 10;418(2):420-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.01.048. Epub 2012 Jan 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22277672
-
[DREAM: a multifunctional transcriptional regulator].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2017 Oct 25;69(5):703-714. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2017. PMID: 29063118 Review. Chinese.
-
[DREAM/Calsenilin/KChIP3: a new multifunctional protein in nervous system].Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2005 Jul;36(3):199-203. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2005. PMID: 16270816 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Rubbing Salt in the Wound: Molecular Evolutionary Analysis of Pain-Related Genes Reveals the Pain Adaptation of Cetaceans in Seawater.Animals (Basel). 2022 Dec 16;12(24):3571. doi: 10.3390/ani12243571. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552490 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupted circadian rhythms and opioid-mediated adverse effects: Bidirectional relationship and putative mechanisms.J Neuroendocrinol. 2025 Sep;37(9):e70065. doi: 10.1111/jne.70065. Epub 2025 Jul 6. J Neuroendocrinol. 2025. PMID: 40619210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polygonum Cuspidatum Alcohol Extract Exerts Analgesic Effects via the MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Oct 19;17:3151-3167. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S420002. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 37876500 Free PMC article.
-
Disease- and headache-specific microRNA signatures and their predicted mRNA targets in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in migraineurs: role of inflammatory signalling and oxidative stress.J Headache Pain. 2022 Sep 2;23(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s10194-022-01478-w. J Headache Pain. 2022. PMID: 36050647 Free PMC article.
-
Omics and Male Infertility: Highlighting the Application of Transcriptomic Data.Life (Basel). 2022 Feb 14;12(2):280. doi: 10.3390/life12020280. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35207567 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

