Impairment of Dendrodendritic Inhibition in the Olfactory Bulb of APP/PS1 Mice
- PMID: 30740049
- PMCID: PMC6357935
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00002
Impairment of Dendrodendritic Inhibition in the Olfactory Bulb of APP/PS1 Mice
Abstract
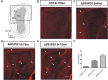
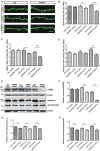
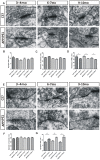
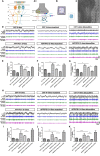
Olfactory dysfunction is an early event in Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, the mechanism underlying the AD-related changes in the olfactory bulb (OB) remains unknown. Granule cells (GCs) in the OB regulate the activity of mitral cells (MCs) through reciprocal dendrodendritic synapses, which is crucial for olfactory signal processing and odor discrimination. Nevertheless, the relationships between the morphological and functional changes of dendrodendritic synapses, particularly the local field potentials (LFPs) as a consequence of olfactory disorders in patients with AD have not been investigated. Here, we studied the morphological and functional changes induced by dendrodendritic inhibition in GCs onto MCs in the OB of amyloid precursor protein (APP)/PS1 mice and age-matched control mice during aging, particular, we focused on the effects of olfactory disorder in the dendrodendritic synaptic structures and the LFPs. We found that olfactory disorder was associated with increased amyloid-β (Aβ) deposits in the OB of APP/PS1 mice, and those mice also exhibited abnormal changes in the morphology of GCs and MCs, a decreased density of GC dendritic spines and impairments in the synaptic interface of dendrodendritic synapses between GCs and MCs. In addition, the aberrant enhancements in the γ oscillations and firing rates of MCs in the OB of APP/PS1 mice were recorded by multi-electrode arrays (MEAs). The local application of a GABAAR agonist nearly abolished the aberrant increase in γ oscillations in the external plexiform layer (EPL) at advanced stages of AD, whereas a GABAAR antagonist aggravated the γ oscillations. Based on our findings, we concluded that the altered morphologies of the synaptic structures of GCs, the dysfunction of reciprocal dendrodendritic synapses between MCs and GCs, and the abnormal γ oscillations in the EPL might contribute to olfactory dysfunction in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; dendrodendritic inhibition; olfactory bulb; olfactory dysfunction; γ oscillations.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Olfactory deficit is associated with mitral cell dysfunction in the olfactory bulb of P301S tau transgenic mice.Brain Res Bull. 2019 May;148:34-45. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.03.006. Epub 2019 Mar 19. Brain Res Bull. 2019. PMID: 30902575
-
Enhancing GABAergic signaling ameliorates aberrant gamma oscillations of olfactory bulb in AD mouse models.Mol Neurodegener. 2021 Mar 4;16(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s13024-021-00434-7. Mol Neurodegener. 2021. PMID: 33663578 Free PMC article.
-
An early dysregulation of FAK and MEK/ERK signaling pathways precedes the β-amyloid deposition in the olfactory bulb of APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Proteomics. 2016 Oct 4;148:149-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.07.032. Epub 2016 Aug 3. J Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27498392
-
Computing with dendrodendritic synapses in the olfactory bulb.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 Jul;1170:264-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.03899.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. PMID: 19686145 Review.
-
A potential biomarker of preclinical Alzheimer's disease: The olfactory dysfunction and its pathogenesis-based neural circuitry impairments.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022 Jan;132:857-869. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.11.009. Epub 2021 Nov 20. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022. PMID: 34810025 Review.
Cited by
-
Ginsenoside Rg1 alleviates learning and memory impairments and Aβ disposition through inhibiting NLRP1 inflammasome and autophagy dysfunction in APP/PS1 mice.Mol Med Rep. 2023 Jan;27(1):6. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12893. Epub 2022 Nov 11. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 36367174 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM67 Implicates in Regulating the Homeostasis and Synaptic Development of Mitral Cells in the Olfactory Bulb.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 30;24(17):13439. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713439. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686246 Free PMC article.
-
Neurogenesis dynamics in the olfactory bulb: deciphering circuitry organization, function, and adaptive plasticity.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Jun 1;20(6):1565-1581. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00312. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 38934393 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory deficits in aging and Alzheimer's-spotlight on inhibitory interneurons.Front Neurosci. 2024 Dec 16;18:1503069. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1503069. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39737436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Olfactory Three-Needle Electroacupuncture Improved Synaptic Plasticity and Gut Microbiota of SAMP8 Mice by Stimulating Olfactory Nerve.Chin J Integr Med. 2024 Aug;30(8):729-741. doi: 10.1007/s11655-023-3614-3. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Chin J Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 37999886
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

