Anti-arrhythmic Cardiac Phenotype Elicited by Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia Is Associated With Alterations in Connexin-43 Expression, Phosphorylation, and Distribution
- PMID: 30740090
- PMCID: PMC6357219
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00789
Anti-arrhythmic Cardiac Phenotype Elicited by Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia Is Associated With Alterations in Connexin-43 Expression, Phosphorylation, and Distribution
Abstract
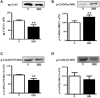
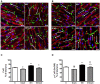
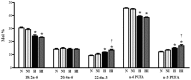
Remodeling of the cellular distribution of gap junctions formed mainly by connexin-43 (Cx43) can be related to the increased incidence of cardiac arrhythmias. It has been shown that adaptation to chronic intermittent hypobaric hypoxia (IHH) attenuates the incidence and severity of ischemic and reperfusion ventricular arrhythmias and increases the proportion of anti-arrhythmic n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFA) in heart phospholipids. Wistar rats were exposed to simulated IHH (7,000 m, 8-h/day, 35 exposures) and compared with normoxic controls (N). Cx43 expression, phosphorylation, localization and n-3 PUFA proportion were analyzed in left ventricular myocardium. Compared to N, IHH led to higher expression of total Cx43, its variant phosphorylated at Ser368 [p-Cx43(Ser368)], which maintains "end to end" communication, as well as p-Cx43(Ser364/365), which facilitates conductivity. By contrast, expression of non-phosphorylated Cx43 and p-Cx43(Ser278/289), attenuating intercellular communication, was lower in IHH than in N. IHH also resulted in increased expression of protein kinase A and protein kinase G while casein kinase 1 did not change compared to N. In IHH group, which exhibited reduced incidence of ischemic ventricular arrhythmias, Cx43 and p-Cx43(Ser368) were more abundant at "end to end" gap junctions than in N group and this difference was preserved after acute regional ischemia (10 min). We further confirmed higher n-3 PUFA proportion in heart phospholipids after adaptation to IHH, which was even further increased by ischemia. Our results suggest that adaptation to IHH alters expression, phosphorylation and distribution of Cx43 as well as cardioprotective n-3PUFA proportion suggesting that the anti-arrhythmic phenotype elicited by IHH can be at least partly related to the stabilization of the "end to end" conductivity between cardiomyocytes during brief ischemia.
Keywords: arrhythmia; brief ischemia; chronic hypoxia; connexin-43; heart; n-3 PUFA.
Figures




References
-
- Sanchez J, Rodriguez-Sinovas A, Fernandez-Sanz C, Ruiz-Meana M, Garcia-Dorado D. Effects of a reduction in the number of gap junction channels or in their conductance on ischemia-reperfusion arrhythmias in isolated mouse hearts. Am J Physiol Heart Circulat Physiol. (2011) 301:2442–53. 10.1152/ajpheart.00540.2011 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

