14-3-3 Protein of Neospora caninum Modulates Host Cell Innate Immunity Through the Activation of MAPK and NF-κB Pathways
- PMID: 30740096
- PMCID: PMC6355710
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00037
14-3-3 Protein of Neospora caninum Modulates Host Cell Innate Immunity Through the Activation of MAPK and NF-κB Pathways
Abstract
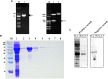
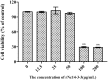
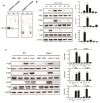
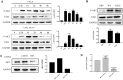
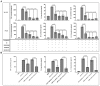
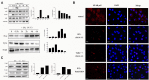
Neospora caninum is an obligate intracellular apicomplexan parasite, the etiologic agent of neosporosis, and a major cause of reproductive loss in cattle. There is still a lack of effective prevention and treatment measures. The 14-3-3 protein is a widely expressed acidic protein that spontaneously forms dimers within apicomplexan parasites. This protein has been isolated and sequenced in many parasites; however, there are few reports about the N. caninum 14-3-3 protein. Here, we successfully expressed and purified a recombinant fusion protein of Nc14-3-3 (rNc14-3-3) and prepared a polyclonal antibody. Immunofluorescence and immunogold electron microscopy studies of tachyzoites or N. caninum-infected cells suggested that 14-3-3 was localized in the cytosol and the membrane. Western blotting analysis indicated that rNc14-3-3 could be recognized by N. caninum-infected mouse sera, suggesting that 14-3-3 may be an infection-associated antigen that is involved in the host immune response. We demonstrated that rNc14-3-3 induced cytokine expression by activating the MAPK and AKT signaling pathways, and inhibitors of p38, ERK, JNK, and AKT could significantly decrease the production of IL-6, IL-12p40, and TNF-α. In addition, phosphorylated nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB/p65) was observed in wild-type peritoneal macrophages (PMs) treated with rNc14-3-3, and the protein level of NF-κB/p65 was reduced in the cytoplasm but increased correspondingly in the nucleus after 2 h of treatment. These results were also observed in deficient in TLR2-/- PMs. Taken together, our results indicated that the N. caninum 14-3-3 protein can induce effective immune responses and stimulate cytokine expression by activating the MAPK, AKT, and NF-κB signaling pathways but did not dependent TLR2, suggesting that Nc14-3-3 is a novel vaccine candidate against neosporosis.
Keywords: 14-3-3; AKT; MAPK; Neospora caninum; cytokines; immune protection.
Figures


References
-
- Braun L., Brenier-Pinchart M. P., Yogavel M., Curt-Varesano A., Curt-Bertini R. L., Hussain T., et al. (2013). A Toxoplasma dense granule protein, GRA24, modulates the early immune response to infection by promoting a direct and sustained host p38 MAPK activation. J. Exp. Med. 210 2071–2086. 10.1084/jem.20130103 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Calegari-Silva T. C., Vivarini A. C., Miqueline M., Dos Santos G. R., Teixeira K. L., Saliba A. M., et al. (2015). The human parasite Leishmania amazonensis downregulates iNOS expression via NF-kappaB p50/p50 homodimer: role of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Open Biol. 5:150118. 10.1098/rsob.150118 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

