Isolated Cerebral Alveolar Echinococcosis
- PMID: 30740467
- PMCID: PMC6355661
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofy349
Isolated Cerebral Alveolar Echinococcosis
Abstract
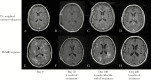
Cerebral alveolar echinococcosis (AE) is rare and mostly associated with liver involvement. We report an exceptional case of a 62-year-old man with a hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia harboring a primary cerebral AE mimicking neurocysticercosis with >100 cerebral lesions and without liver involvement.
Keywords: Echinococcus multilocularis; abscess; cerebral; primary lesion.
Figures

References
-
- Kern P, Menezes da Silva A, Akhan O, et al. The echinococcoses: diagnosis, clinical management and burden of disease. Adv Parasitol 2017; 96:259–369. - PubMed

