TRAIL pathway targeting therapeutics
- PMID: 30740527
- PMCID: PMC6366666
- DOI: 10.1080/23808993.2018.1476062
TRAIL pathway targeting therapeutics
Abstract
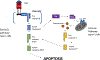
Introduction: Despite decades of focused research efforts, cancer remains a significant cause of morbidity and mortality. Tumor necrosis factor(TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is capable of inducing cell death selectively in cancer cells while sparing normal cells.
Areas covered: In this review, the authors cover TRA therapy and strategies that have been undertaken to improve their efficacy, as well as unconventional approaches to TRAIL pathway activation including TRAIL-inducing small molecules. They also discuss mechanisms of resistance to TRAIL and the use of combination strategies to overcome it.
Expert commentary: Targeting the TRAIL pathway has been of interest in oncology, and although initial clinical trials of TRAIL receptor agonists (TRAs) showed limitations, novel approaches represent the future of TRAIL-based therapy.
Keywords: Apoptosis; DISC; Imipridone; TRAIL; TRAIL-R agonist; apoptosome; atrimer; cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Hengartner MO, The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature, 2000. 12(407): p. 770–776. - PubMed
-
- Youle RJ and Strasser A, The BCL-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2008. 9. - PubMed
-
- Cain K, Bratton SB, Langlais C, et al. , Apaf-1 Oligomerizes into Biologically Active 700-kDa and Inactive 1.4-MDa Apoptosome Complexes. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2000. 275(9): p. 6067–6070. - PubMed
-
- Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Ruppert S, et al. , Induction of Apoptosis by Apo-2 Ligand, a New Member of the Tumor Necrosis Factor Cytokine Family. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1996. 271(22): p. 12687–12690. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
