Aberrant Expression of p14ARF in Human Cancers: A New Biomarker?
- PMID: 30740529
- PMCID: PMC6364748
- DOI: 10.4103/tme.tme_24_17
Aberrant Expression of p14ARF in Human Cancers: A New Biomarker?
Abstract
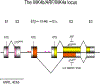
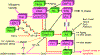
The ARF and INK4a genes are located on the CDKN2a locus, both showing tumor suppressive activity. ARF has been shown to monitor potentially harmful oncogenic signalings, making early stage cancer cells undergo senescence or programmed cell death to prevent cancer. Conversely, INK4a detects both aging and incipient cancer cell signals, and thus these two gene functions are different. The efficiency of detection of oncogenic signals is more efficient for the for the former than the latter in the mouse system. Both ARF and INK4a genes are inactivated by gene deletion, promoter methylation, frame shift, aberrant splicing although point mutations for the coding region affect only the latter. Recent studies show the splicing alterations that affect only ARF or both ARF and INK4a genes suggesting that ARF is inactivated in human tumors more frequently than what was previously thought. The ARF gene is activated by E2Fs and Dmp1 transcription factors while it is repressed by Bmi1, Tbx2/3, Twist1, and Pokemon nuclear proteins. It is also regulated at protein levels by Arf ubiquitin ligase named ULF, MKRN1, and Siva1. The prognostic value of ARF overexpression is controversial since it is induced in early stage cancer cells to eliminate pre-malignant cells (better prognosis); however, it may also indicate that the tumor cells have mutant p53 associated with worse prognosis. The ARF tumor suppressive protein can be used as a biomarker to detect early stage cancer cells as well as advanced stage tumors with p53 inactivation.
Keywords: ARF; BMI1; CDKN2a; DMP1 (DMTF1); E2F; INK4a; biomarker; cancer; expression; p53; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Maggi LB Jr, Winkeler CL, Miceli AP, Apicelli AJ, Brady SN, Kuchenreuther MJ, et al. ARF tumor suppression in the nucleolus. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014;1842:831–9. - PubMed
-
- Quelle DE, Zindy F, Ashmun RA, Sherr CJ. Alternative reading frames of the INK4a tumor suppressor gene encode two unrelated proteins capable of inducing cell cycle arrest. Cell 1995;83:993–1000. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
