Hemoglobin targets for the anemia in patients with dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials
- PMID: 30741617
- PMCID: PMC6282462
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2018.1532909
Hemoglobin targets for the anemia in patients with dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Anemia is extremely common among dialysis patients and underlies some of the symptoms associated with reduced kidney function, including fatigue, depression, reduced exercise tolerance, and dyspnea.
Objectives: A clearer cognition of the prognosistic impact of hemoglobin (Hb) or hematocrit (Hct) target for the outcomes of dialysis patients is urgent. This article aims to establish the suitable hemoglobin in order to provide clinical guidance.
Methods: MEDLINE, EmBase, the Cochrane Library and other databases were searched with both MeSH terms and keywords to gather randomized controlled trials that assessed all-cause mortality, cardiovascular events, fistula thrombosis, infectious diseases and transfusion among dialysis-dependent patients using erythropoiesis-stimulating agents. The meta-analysis was accomplished via Revman 5.3 version.
Findings: Totally, nine eligible studies were included, with study subjects involving 3228 patients. There was a significantly higher risk of fistula thrombosis without heterogeneity (RR 1.34, 95% CI 1.15-1.55; p < 0.05) in the higher Hb target group than in the lower Hb target group in the fixed effects model. However, no significant difference was found in all-cause mortality in the fixed effects model (RR 1.09, 95% CI 0.93-1.27; p = 0.30), cardiovascular events (RR 0.77, 95% CI 0.31-1.92; p = 0.58), infectious diseases (RR 0.69, 95% CI 0.24-1.96; p = 0.49) and transfusion (RR 0.92, 95% CI 0.42-1.99; p = 0.82) in the random effects model between the higher Hb target group and the lower Hb target group.
Discussion: The results favor lower Hb target. To target lower Hb target when treating dialysis patients with anemia may decrease the risk of fistula thrombosis without increasing the risk of death, cardiovascular events, infectious diseases and transfusion.
Keywords: Anemia; dialysis; meta-analysis; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures


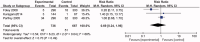



Similar articles
-
Therapeutic targets for the anemia of predialysis chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials.J Investig Med. 2019 Aug;67(6):1002-1008. doi: 10.1136/jim-2018-000915. Epub 2019 Feb 11. J Investig Med. 2019. PMID: 30755495
-
Economic and quality of life burden of anemia on patients with CKD on dialysis: a systematic review.J Med Econ. 2019 Jun;22(6):593-604. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2019.1588738. Epub 2019 Mar 27. J Med Econ. 2019. PMID: 30813807
-
Meta-analysis: erythropoiesis-stimulating agents in patients with chronic kidney disease.Ann Intern Med. 2010 Jul 6;153(1):23-33. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-153-1-201007060-00252. Epub 2010 Jun 24. Ann Intern Med. 2010. PMID: 20439566 Review.
-
Is there an established hemoglobin target range for patients undergoing chronic dialysis?Semin Dial. 2018 Jul;31(4):415-419. doi: 10.1111/sdi.12683. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Semin Dial. 2018. PMID: 29509320 Review.
-
A Phase 3, Multicenter, Randomized, Two-Arm, Open-Label Study of Intermittent Oral Dosing of Roxadustat for the Treatment of Anemia in Japanese Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agent-Naïve Chronic Kidney Disease Patients Not on Dialysis.Nephron. 2020;144(8):372-382. doi: 10.1159/000508100. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Nephron. 2020. PMID: 32580188 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Interdialytic Weight Gain Effects on Hemoglobin Concentration and Cardiovascular Events.Kidney Int Rep. 2020 Jul 27;5(10):1670-1678. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2020.07.027. eCollection 2020 Oct. Kidney Int Rep. 2020. PMID: 33102959 Free PMC article.
-
Erratum: Interdialytic Weight Gain Effects on Hemoglobin Concentration and Cardiovascular Events.Kidney Int Rep. 2021 May 20;6(7):1999-2007. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2021.05.016. eCollection 2021 Jul. Kidney Int Rep. 2021. PMID: 34307997 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Low Hemoglobin on Body Composition, Strength, and Redox Status of Older Hemodialysis Patients Following Resistance Training.Front Physiol. 2021 Mar 10;12:619054. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.619054. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33776788 Free PMC article.
-
Association between haemoglobin concentration and intradialytic hypotension in patients undergoing maintenance haemodialysis: a retrospective cohort study.BMJ Open. 2022 Aug 26;12(8):e064026. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-064026. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 36028275 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of "CKD-PeriDialysis"-the Periods Prior to and in the Early-Stage of Initial Dialysis.Kidney Int Rep. 2022 Dec 12;7(12 Suppl):S531-S558. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.10.001. eCollection 2022 Dec. Kidney Int Rep. 2022. PMID: 36567827 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bethesda M. USRDS annual data report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. United States Renal Data System, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. 2014:188–210.
-
- McGonigle RJ, Wallin JD, Shadduck RK, et al. . Erythropoietin deficiency and inhibition of erythropoiesis in renal insufficiency. Kidney international. 1984. Feb;25(2):437–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
