NADP+ is an endogenous PARP inhibitor in DNA damage response and tumor suppression
- PMID: 30741937
- PMCID: PMC6370829
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-08530-5
NADP+ is an endogenous PARP inhibitor in DNA damage response and tumor suppression
Abstract
ADP-ribosylation is a unique posttranslational modification catalyzed by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs) using NAD+ as ADP-ribose donor. PARPs play an indispensable role in DNA damage repair and small molecule PARP inhibitors have emerged as potent anticancer drugs. However, to date, PARP inhibitor treatment has been restricted to patients with BRCA1/2 mutation-associated breast and ovarian cancer. One of the major challenges to extend the therapeutic potential of PARP inhibitors to other cancer types is the absence of predictive biomarkers. Here, we show that ovarian cancer cells with higher level of NADP+, an NAD+ derivative, are more sensitive to PARP inhibitors. We demonstrate that NADP+ acts as a negative regulator and suppresses ADP-ribosylation both in vitro and in vivo. NADP+ impairs ADP-ribosylation-dependent DNA damage repair and sensitizes tumor cell to chemically synthesized PARP inhibitors. Taken together, our study identifies NADP+ as an endogenous PARP inhibitor that may have implications in cancer treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
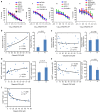
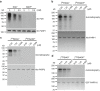
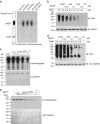
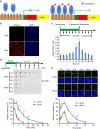
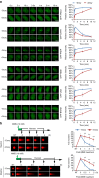
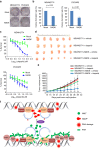
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

