Biomarkers of Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 30742783
- PMCID: PMC7879424
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-020518-114605
Biomarkers of Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
The current unidimensional paradigm of kidney disease detection is incompatible with the complexity and heterogeneity of renal pathology. The diagnosis of kidney disease has largely focused on glomerular filtration, while assessment of kidney tubular health has notably been absent. Following insult, the kidney tubular cells undergo a cascade of cellular responses that result in the production and accumulation of low-molecular-weight proteins in the urine and systemic circulation. Modern advancements in molecular analysis and proteomics have allowed the identification and quantification of these proteins as biomarkers for assessing and characterizing kidney diseases. In this review, we highlight promising biomarkers of kidney tubular health that have strong underpinnings in the pathophysiology of kidney disease. These biomarkers have been applied to various specific clinical settings from the spectrum of acute to chronic kidney diseases, demonstrating the potential to improve patient care.
Keywords: AKI; CKD; acute kidney injury; biomarkers; chronic kidney disease; kidney.
Figures

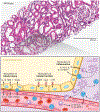

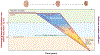
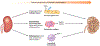
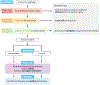
References
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS, Morimatsu H, et al. 2005. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA 294:813–18 - PubMed
-
- Kampmann J, Siersbaek-Nielsen K, Kristensen M, Hansen JM. 1974. Rapid evaluation of creatinine clearance. Acta Med. Scand 196:517–20 - PubMed
-
- Nickolas TL, Barasch J, Devarajan P. 2008. Biomarkers in acute and chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens 17:127–32 - PubMed
-
- Bosch JP. 1995. Renal reserve: a functional view of glomerular filtration rate. Semin. Nephrol 15:381–85 - PubMed
-
- Herrera J, Rodríguez-Iturbe B. 1998. Stimulation of tubular secretion of creatinine in health and in conditions associated with reduced nephron mass. Evidence for a tubular functional reserve. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant 13:623–29 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

