Antioxidant Activities of Solanum Nigrum L. Leaf Extracts Determined in in vitro Cellular Models
- PMID: 30744041
- PMCID: PMC6406898
- DOI: 10.3390/foods8020063
Antioxidant Activities of Solanum Nigrum L. Leaf Extracts Determined in in vitro Cellular Models
Abstract
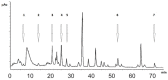
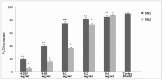
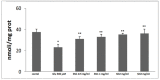
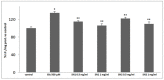
Several medicinal foods abound in traditional medicine with antioxidant potentials that could be of importance for the management of several diseases but with little or no scientific justification to substantiate their use. Thus, the objective of this study was the assessment of the antioxidant effect of two leave extracts of Solanum nigrum L. (SN), which is a medicinal plant member of the Solanaceae family, mainly used for soup preparation in different parts of the world. Then methanolic/water (80:20) (SN1) and water (SN2) leaves extracts were prepared. The total polyphenolic content and the concentration of phenolic acids and flavones compounds were determined. In order to verify whether examined extracts were able to restore the oxidative status, modified by glutamate in primary cultures of astrocytes, the study evaluated the glutathione levels, the intracellular oxidative stress, and the cytotoxicity of SN1 and SN2 extracts. Both extracts were able to quench the radical in an in vitro free cellular system and restore the oxidative status in in vitro primary cultures of rat astroglial cells exposed to glutamate. These extracts prevented the increase in glutamate uptake and inhibited glutamate excitotoxicity, which leads to cell damage and shows a notable antioxidant property.
Keywords: Solanum nigrum L. leave extracts; antioxidant activity; functional food; natural products.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest and the founder added the requested detail. The funder M.R. had roles in methodology, validation, formal analysis, visualization and the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Jagatheeswari D., Bharathi T., Sheik Jahabar Ali H. Black Night Shade (Solanum nigrum L.)-An Updated Overview. Int. J. Pharm. Biol. Arch. 2013;4:288–295.
-
- Akubugwo I.E., Obasi A.N., Ginika S.C. Nutritional Potential of the Leaves and Seeds of Black Nightshade-Solanum nigrum L. Var virginicum from Afikpo-Nigeria. Pak. J. Nutr. 2007;6:323–326. doi: 10.3923/pjn.2007.323.326. - DOI
-
- Jain R., Sharma A., Gupta S., Sarethy I.P., Gabrani R. Solanum nigrum: Current perspectives on therapeutic properties. Altern. Med. Rev. 2011;16:78–85. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

