Structure and Function of IP3 Receptors
- PMID: 30745293
- PMCID: PMC6442203
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a035063
Structure and Function of IP3 Receptors
Abstract
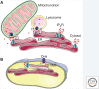
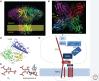
Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors (IP3Rs), by releasing Ca2+ from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of animal cells, allow Ca2+ to be redistributed from the ER to the cytosol or other organelles, and they initiate store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE). For all three IP3R subtypes, binding of IP3 primes them to bind Ca2+, which then triggers channel opening. We are now close to understanding the structural basis of IP3R activation. Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release regulated by IP3 allows IP3Rs to regeneratively propagate Ca2+ signals. The smallest of these regenerative events is a Ca2+ puff, which arises from the nearly simultaneous opening of a small cluster of IP3Rs. Ca2+ puffs are the basic building blocks for all IP3-evoked Ca2+ signals, but only some IP3 clusters, namely those parked alongside the ER-plasma membrane junctions where SOCE occurs, are licensed to respond. The location of these licensed IP3Rs may allow them to selectively regulate SOCE.
Copyright © 2019 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Alzayady KJ, Sebe-Pedros A, Chandrasekhar R, Wang L, Ruiz-Trillo I, Yule DI. 2015. Tracing the evolutionary history of inositol, 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate receptor: Insights from analyses of Capsaspora owczarzaki Ca2+ release channel orthologs. Mol Biol Evol 32: 2236–2253. 10.1093/molbev/msv098 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
