UDP-glucose Dehydrogenase: The First-step Oxidation Is an NAD+-dependent Bimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction (SN2)
- PMID: 30745825
- PMCID: PMC6367545
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.28904
UDP-glucose Dehydrogenase: The First-step Oxidation Is an NAD+-dependent Bimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction (SN2)
Abstract
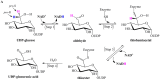
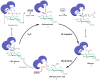
UDP-glucose dehydrogenase (UGDH) catalyzes the conversion of UDP-glucose to UDP-glucuronic acid by NAD+-dependent two-fold oxidation. Despite extensive investigation into the catalytic mechanism of UGDH, the previously proposed mechanisms regarding the first-step oxidation are somewhat controversial and inconsistent with some biochemical evidence, which instead supports a mechanism involving an NAD+-dependent bimolecular nucleophilic substitution (SN2) reaction. To verify this speculation, the essential Cys residue of Streptococcus zooepidemicus UGDH (SzUGDH) was changed to an Ala residue, and the resulting Cys260Ala mutant and SzUGDH were then co-expressed in vivo via a single-crossover homologous recombination method. Contrary to the previously proposed mechanisms, which predict the formation of the capsular polysaccharide hyaluronan, the resulting strain instead produced an amide derivative of hyaluronan, as validated via proteinase K digestion, ninhydrin reaction, FT-IR and NMR. This result is compatible with the NAD+-dependent SN2 mechanism.
Keywords: NAD+-dependent; UDP-glucose dehydrogenase; bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction (SN2); catalytic mechanism; two-fold oxidation.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



References
-
- Strominger JL, Kalckar HM, Axelrod J. et al. Enzymatic oxidation of uridine diphosphate glucose to uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid. J Am Chem Soc. 1954;76:6411–6412.
-
- Walsh EC, Stainier DY. UDP-glucose dehydrogenase required for cardiac valve formation in zebrafish. Science. 2001;293:1670–1673. - PubMed
-
- Johansson H, Sterky F, Amini B. et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding poplar UDP-glucose dehydrogenase, a key gene of hemicellulose/pectin formation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;1576:53–58. - PubMed
-
- Griffith CL, Klutts JS, Zhang L. et al. UDP-glucose dehydrogenase plays multiple roles in the biology of the pathogenic fungus Cryptococcus neoformans. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:51669–51676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

