Efficacy of 10% Potassium Hydroxide Solution Versus 10% Salicylic Acid Ointment in Treatment of Molluscum Contagiosum - the Low - Cost Dermatologic Therapy in Vietnam
- PMID: 30745977
- PMCID: PMC6364743
- DOI: 10.3889/oamjms.2019.090
Efficacy of 10% Potassium Hydroxide Solution Versus 10% Salicylic Acid Ointment in Treatment of Molluscum Contagiosum - the Low - Cost Dermatologic Therapy in Vietnam
Abstract
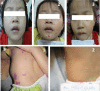
Background: Molluscum contagiosum is a common viral disease primarily affecting children.
Aim: The objective is to compare the efficacy of 10% potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution versus 10% salicylic pomade in the treatment of molluscum contagiosum.
Methods: Clinical trials on 70 patients were randomised into 2 groups: 39 patients treated with 10% KOH solution and 31 patients treated with 10% salicylic pomade. The evaluation was based on the complete clearance of lesions, side effects and complications of the drug.
Results: The clearance of all lesions after 2, 4, 6, 8 weeks of treatment in both groups were 7.7%; 23.1%; 53.8%; 79.5% and 0%; 3.2%, 9.7% 22.6%, respectively (p < 0.05). Side effects were seen in both groups include burning (76.9% versus 19.4%; p < 0.05); redness (59% versus 14%; p < 0.01); desquamation (12.8% versus 19.3%; p < 0.05).
Conclusion: The efficacy of KOH solution in the treatment of MC was better than that of salicylic pomade and both products are safe, effective, and easy to apply at home.
Keywords: Molluscum contagiosum; Potassium Hydroxide; Salicylic pomade.
Figures
References
-
- Dave D, Abdelmaksoud A. Glycolic acid cream for the treatment of molluscum contagiosum. Dermatologic therapy. 2018;31(5):e12630. https://doi.org/10.1111/dth.12630 PMid:30155957. - PubMed
-
- Metkar A, Pande S, Khopkar U. An open, nonrandomized, comparative study of imiquimod 5% cream versus 10% potassium hydroxide solution in the treatment of molluscum contagiosum. Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology, and Leprology. 2008;74(6):614–8. https://doi.org/10.4103/0378-6323.45104. - PubMed
-
- Seo SH, Chin HW, Jeong DW, Sung HW. An open, randomized, comparative clinical and histological study of imiquimod 5% cream versus 10% potassium hydroxide solution in the treatment of molluscum contagiosum. Annals of dermatology. 2010;22(2):156–62. https://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2010.22.2.156 PMid:20548905 PMCid:PMC2883417. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mahajan BB, Pall A, Gupta RR. Topical 20% KOH-An effective therapeutic modality for moluscum contagiosum in children. Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology, and Leprology. 2003;69(2):175–7. PMid:17642872. - PubMed
-
- Leslie KS, Dootson G, Sterling JC. Topical salicylic acid gel as a treatment for molluscum contagiosum in children. Journal of dermatological treatment. 2005;16(5-6):336–40. https://doi.org/10.1080/09546630500430521 PMid:16428156. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources