Outcomes in Older Kidney Transplant Recipients After Prior Nonkidney Transplants
- PMID: 30747853
- PMCID: PMC6679821
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002596
Outcomes in Older Kidney Transplant Recipients After Prior Nonkidney Transplants
Abstract
Background: Recipients of nonkidney solid organ transplants (nkSOT) are living longer, and 11%-18% will develop end stage renal disease (ESRD). While our general inclination is to treat nkSOT recipients who develop ESRD with a kidney transplant (KT), an increasing number are developing ESRD at an older age where KT may not be the most appropriate treatment. It is possible that the risk of older age and prior nkSOT might synergize to make KT too risky, but this has never been explored.
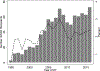
Methods: To examine death-censored graft loss and mortality for KT recipients with and without prior nkSOT, we used Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients data to identify 42 089 older (age ≥65) KT recipients between 1995 and 2016. Additionally, to better understand treatment options for these patients and survival benefit of KT, we identified 5023 older (age ≥65) with prior nkSOT recipients listed for subsequent KT, of whom 863 received transplants.
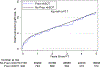
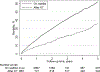
Results: Compared with 41 159 older KT recipients without prior nkSOT, death-censored graft loss was similar (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR]: 1.13, 95% CI: 0.93-1.37, P = 0.2), but mortality (aHR: 1.40, 95% CI: 1.28-1.54, P < 0.001) was greater for older KT recipients with prior nkSOT. Nonetheless, in a survival benefit model (survival with versus without the transplant), among older prior nkSOT recipients, KT decreased the risk of mortality by more than half (aHR: 0.47, 95% CI: 0.42-0.54, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Older prior nkSOT recipients who subsequently develop ESRD derive survival benefit from KT, but graft longevity is limited by overall survival in this population. These findings can help guide patient counseling for this challenging population.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Pushing the Age Envelope: Kidney Transplantation for Elderly Patients With Prior Nonkidney Solid Organ Transplants.Transplantation. 2019 Nov;103(11):2221-2222. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002595. Transplantation. 2019. PMID: 30747846 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wilkinson AH, Cohen DJ. Renal failure in the recipients of nonrenal solid organ transplants. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10(5):1136–1144. - PubMed
-
- Ojo AO, Held PJ, Port FK, et al. Chronic renal failure after transplantation of a nonrenal organ. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(10):931–940. - PubMed
-
- Gonwa TA, Mai ML, Melton LB, et al. End-stage renal disease (ESRD) after orthotopic liver transplantation (OLTX) using calcineurin-based immunotherapy: risk of development and treatment. Transplantation. 2001;72(12):1934–1939. - PubMed
-
- Chandrakantan A, de Mattos AM, Naftel D, Crosswy A, Kirklin J, Curtis JJ. Increasing referral for renal transplant evaluation in recipients of nonrenal solid-organ transplants: a single-center experience. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;1(4):832–836. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

